Review
History
• Suffered from right limb weakness accompanied with aphasia for 4 hours.
• Medical history: No HTN nor DM nor smoking cigarettes. Alcohol consumption for 20 years.
• 神经查体:NHISS 17 (提问2+指令2+凝视2+右上肢4+右下肢4+语言3)。发病2h内予静脉溶栓,但溶栓后患者无缓解。

图 1. 头颅CT平扫未见出血,左侧A1及M1段走行区高密度提示栓塞。Aspect评分9。

Figure 2 . CTA revealed left ICA from cervical to petrosal segment
occlusion, and left A1 plus M1 segment occlusion.
图 2. CTA提示左侧颈内动脉颈段至岩骨段闭塞,左侧A1及M1段闭塞。
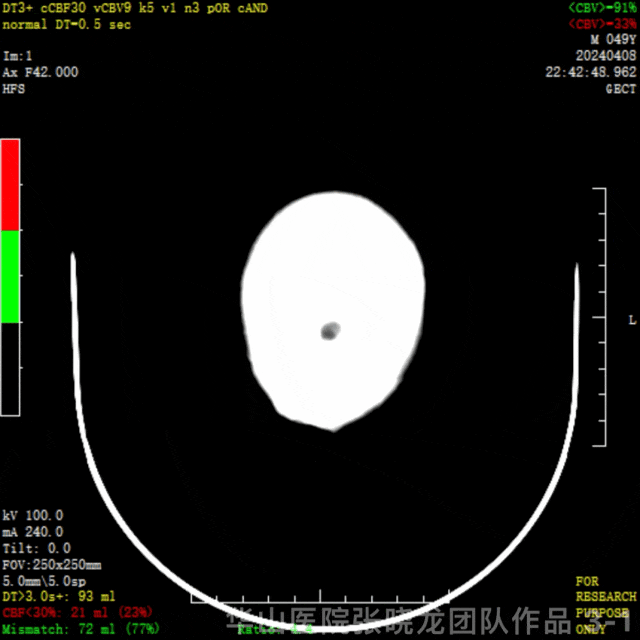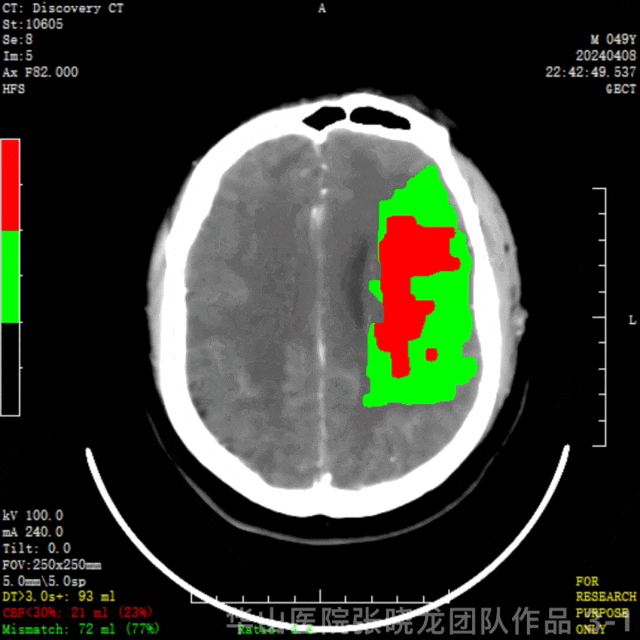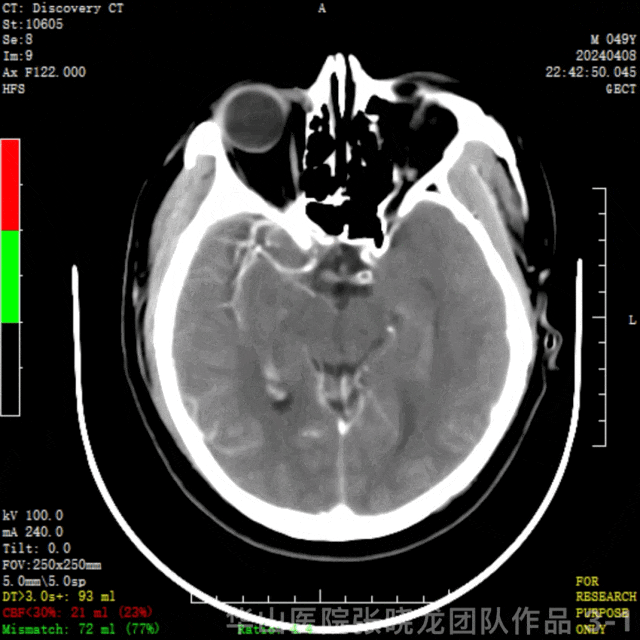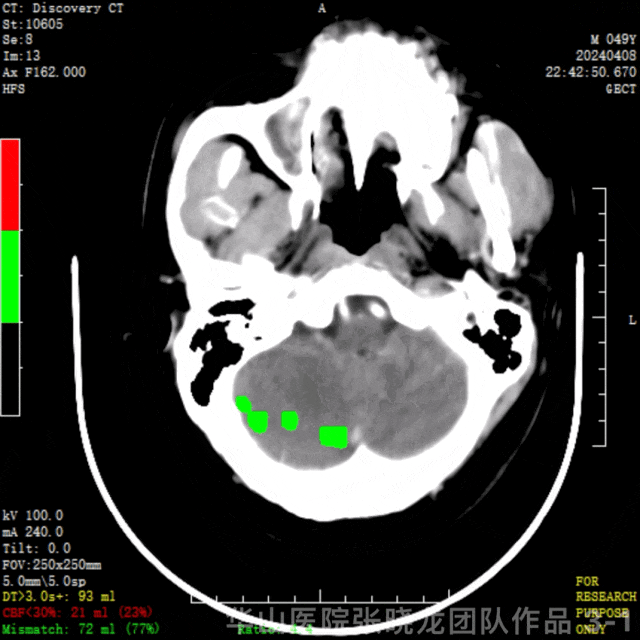

图 3 GIF. CTP示左侧顶颞叶低灌注,左侧半球核心梗死21ml(23%),缺血半暗带72ml(77%)。
1
Indications
•Onset of the acute ischemic stoke within 4 hours.
•After Intravenous thrombolysis, symptoms did not relieve.
•NCCT: M1 and A1 high intensity sign indicated embolism, Aspect ratio 9.
•CTA: Left ICA cervical and petrosal segment occlusion, M1 and A1 segment occlusion.
•发病4小时内。
•静脉溶栓后,患者症状无缓解。
•平扫头颅CT:左侧M1和A1走行区线样高密度提示栓塞,Aspect评分9。
•CTA: 左侧颈内动脉颈段及岩骨段闭塞,左侧M1及A1闭塞,余未见明显高密度影。
•CTP:核心梗死区21ml (23%),缺血半暗带72ml (77%)。 建议行取栓治疗。
2
Strategies
•Roadmap can decrease thrombus migration risk instead of angiography.
•The intracranial vessel should be recanalized as soon as possible.
•Difficulty points: intermediate catheter position.
•90cm长鞘和115cm中间导管有利于A1和M1段的取栓。
•减少造影次数,选择路途示踪,减少血栓逃逸。
•尽快开通颅内闭塞血管。
•难点:中间导管到位。
•危险点:血栓逃逸,术后高灌。
3
Operation
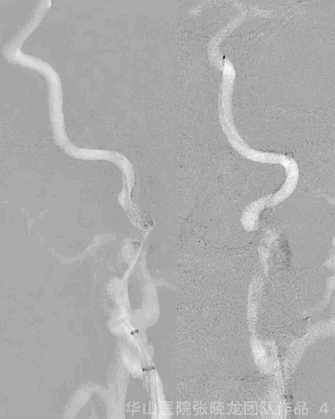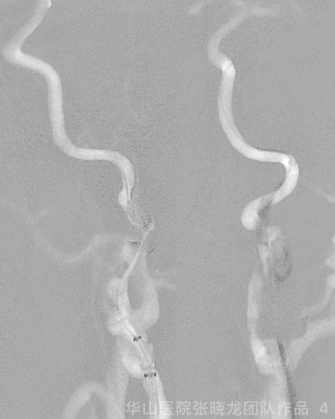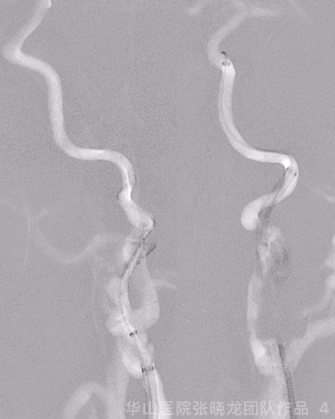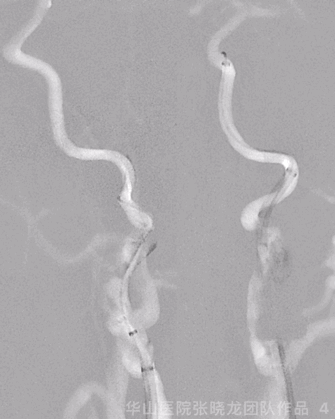
Figure 4 GIF. General anesthesia was performed. 8F sheath was placed into right femoral artery, and 6F 90cm NeuroMax into left ICA initial segment via support of a 125cm MP and 0.035 wire. 6F 115cm Tonbridge was placed into initial segment and roadmap showed cervical segment dissections without thrombus through aspiration. The Tonbridge and long sheath crossed the dissecting segment, with 0.035 wire into real lumen.
图 4 GIF. 全麻后,8F短鞘置于右侧股动脉,选用6F 90cm NeuroMax长鞘在125cm MP和0.035导丝支撑下置于左侧颈内动脉起始部。6F 115cm Tonbridge中间导管置于左侧颈内动脉起始部路图证实颈段夹层,抽吸未见血栓。将中间导管及长鞘在导丝支撑下通过夹层段,0.035导丝位于真腔 。
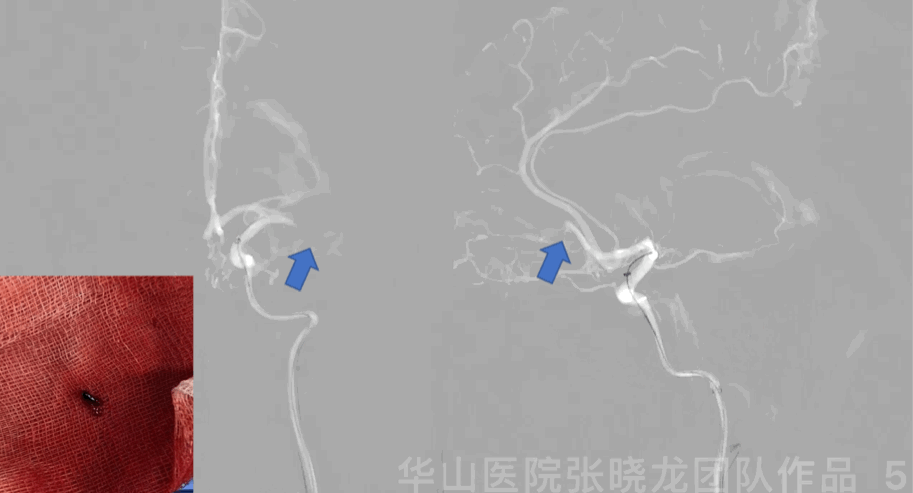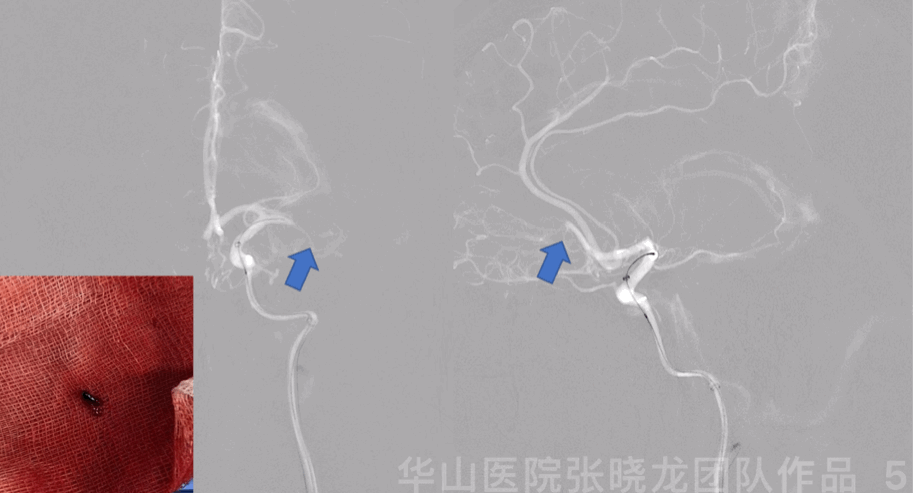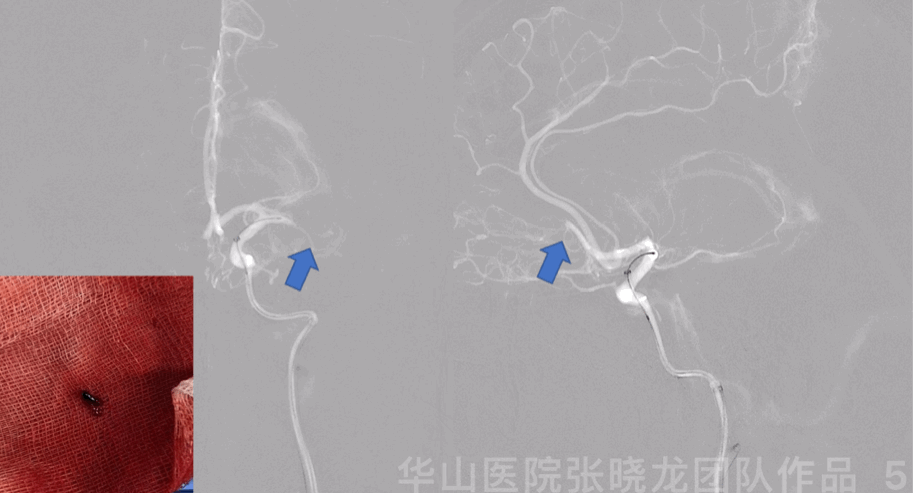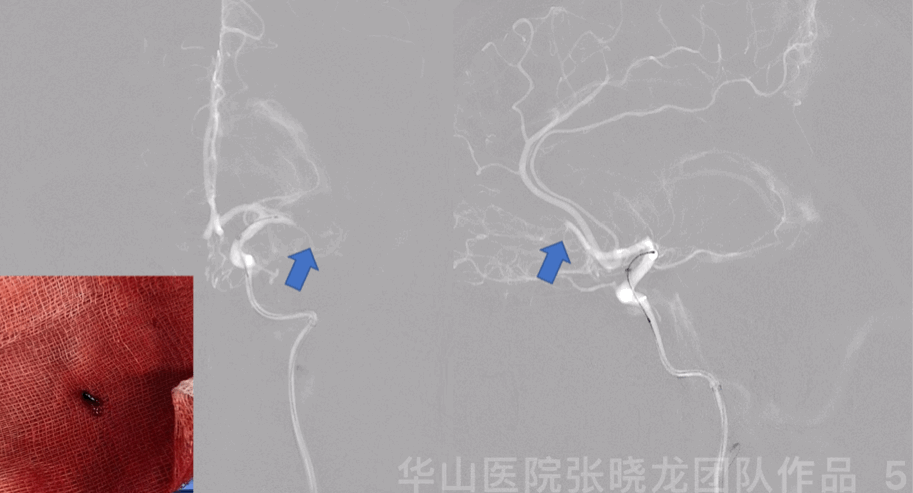
Figure 5 GIF. Roadmap showed left middle cerebral artery M1 segment and anterior cerebral artery A2 segment occlusion. Prowler plus microcatheter was navigated into left M1 segment via a Synchro-II standard microwire. Intermediate catheter was advanced into left M1 occluded segment with the help of microcatheter and microwire, then aspired red thrombus.
Figure 5 GIF. 路图证实左侧大脑中动脉M1及大脑前动脉A2段闭塞。Prowler plus微导管在Synchro-II standard微导丝支撑下置于大脑中动脉M1段,在微导管及微导丝支撑下将中间导管置于M1闭塞段行负压抽吸,抽吸液内见大量暗红色血栓。

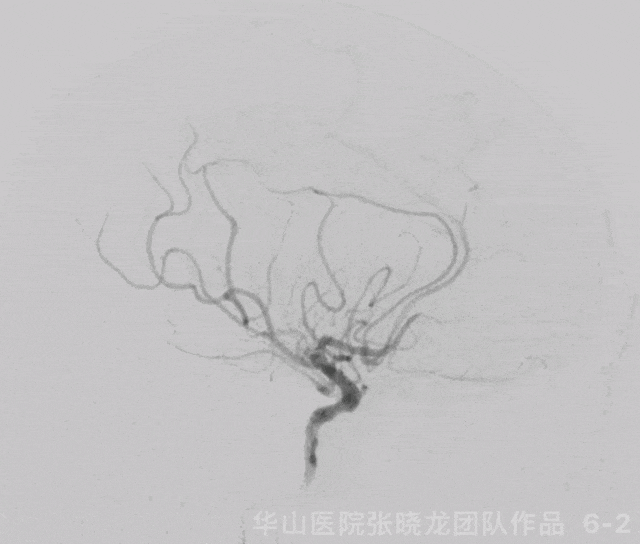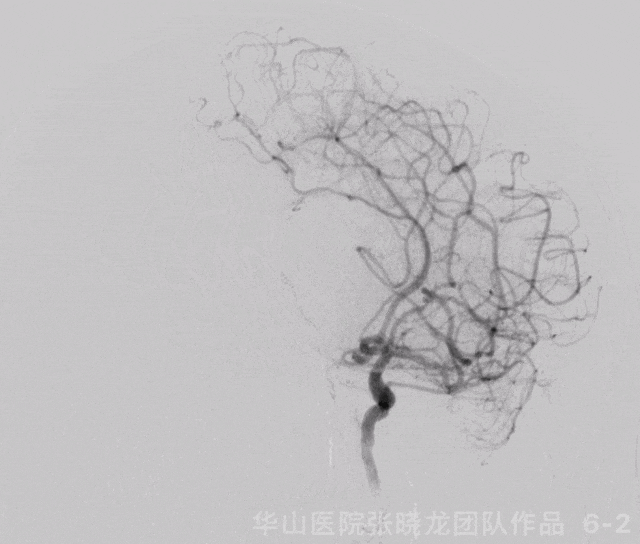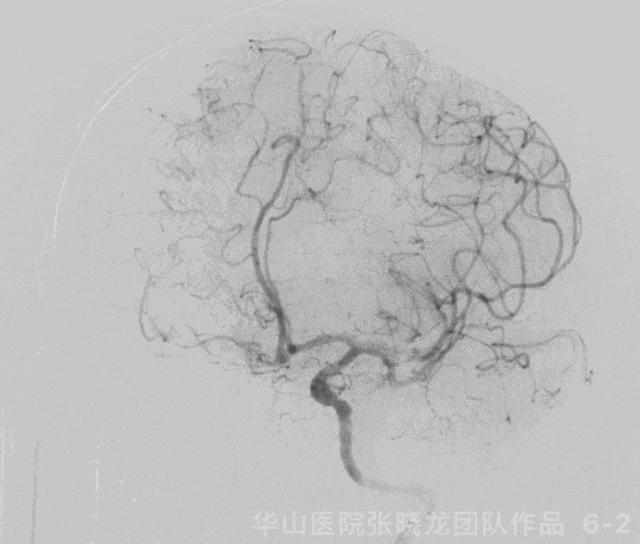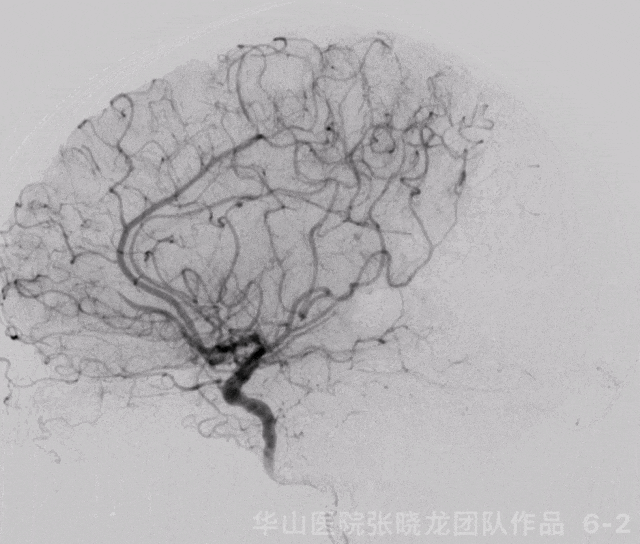
Figure 6 GIF. 复查造影示左侧大脑中动脉M1再通,左侧大脑中动脉下干分支M3段闭塞,左侧A2段闭塞基本同前。经导引导管给予尼莫地平1ml和替罗非班5ml。

Figure 7 GIF. 复查造影示近端造影剂滞留,考虑颈段夹层所致。行全身肝素化。夹层段释放Precise 6*40mm和Precise 7*30mm支架,两枚支架部分重叠释放。复查造影夹层段重建良好。

Figure 8 GIF. 再次复查造影原闭塞段M3部分再通,原A2段血栓逃逸至A3段。

Figure 9 GIF. 后循环向前循环代偿。

Figure 10 GIF. 术后复查Dyna-CT局部高密度影,考虑造影剂滞留。予替罗非班3ml及尼莫地平1ml。术后替罗非班4ml/h继续维持24h。术后未醒麻醉。
4
Post-operative day 1
NE: GCS 15, aphasia and right limb muscle strength improved, right upper limb muscle strength IV-, right lower limb muscle strength V, NHISS 3 (question 1 + Upper right 1 + Language 1) .
神经查体:GCS 15,失语和右侧肌力好转,右上肢肌力IV-,右下肢肌力正常,NHISS 3 (提问 1 + 右上 1 + 语言 1) .
收缩压控制在100-130mmhg。
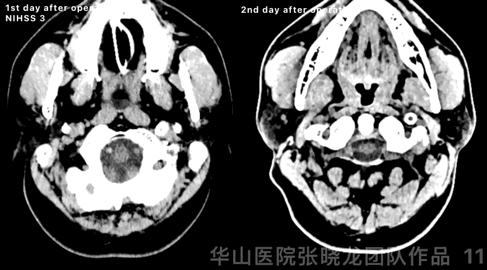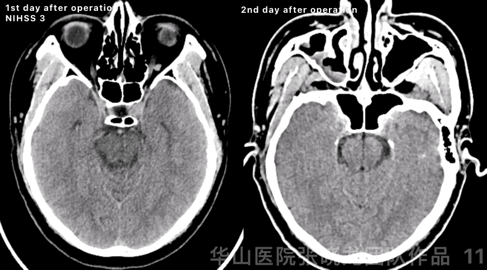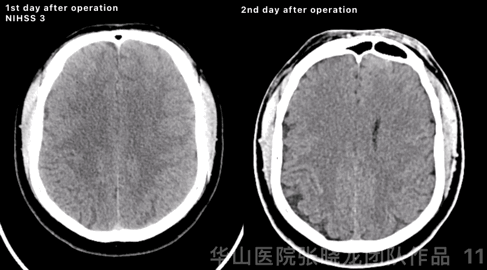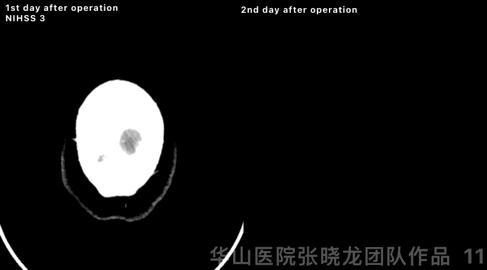
Figure 11 GIF. High density was observed at left basal ganglia from post-operative day 1 CT. Comparing with instant post-operative Dyna-CT, high density region kept stable, while hemorrhage can not be excluded. Stop Tirofiban and aspirin was prescribed. Post-operative day 2 CT scan showed the high density almost absorbed.
Figure 11 GIF. 术后第一天头颅CT平扫示左侧基底节区外囊高密度,尽管与术后即刻对比,高密度范围无增加,但当时仍不能除外出血。予停替罗非班,阿司匹林单抗。术后第2天复查头颅CT示原高密度基本吸收。
Video 1. MRI detected acute infarctions at left frontal lobe, temporal lobe and insula region.
Video 1. 术后第2天头颅MRI示左侧额叶、颞叶及岛叶急性脑梗死。
5
Summary
•The middle-aged male without risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, smoking nor atrial fibrillation, only with a history of drinking, suffered from internal carotid artery occlusion.
•Medical images revealed flame sign at ICA cervical and petrosal segment, therefore left ICA cervical segment and petrosal segment was diagnosed as dissection. The distal part occlusion resulted from the thrombus migration at the cervical segment.
•Middle cerebral artery M1 segment recanalized first after guiding catheter was navigated through dissecting segment. Then stenting reconstruction was preferred for the proximal dissection to reduce the duration of low perfusion ischemia.
•A 90cm proximal sheath combined with a 115cm distal intermediate catheter was selected to ensure proximal stability and facilitate embolism aspiration in M1 segment.
•Roadmap can decrease thrombus migration risk instead of angiography.
•Difficulty points: intermediate catheter position crossing proximal dissecting segment.
•中年男性,无高血压、糖尿病、吸烟、房颤等危险因素,仅有饮酒史,突发颈内动脉闭塞。
•影像学检查提示颈内动脉颈段及岩骨段火焰征,首先考虑颈内动脉夹层。
•在导管通过夹层段后,首先再通大脑中动脉M1段。随后优先对近端夹层进行支架重建,减少低灌注缺血时间。
•90cm长鞘和115cm中间导管有利于近端支撑及远端M1段抽吸取栓。
•减少造影次数,选择路途示踪,减少血栓逃逸。
•难点:中间导管顺利通过夹层段到位。
•危险点:血栓逃逸,术后高灌。
声明:脑医汇旗下神外资讯、神介资讯、脑医咨询、Ai Brain 所发表内容之知识产权为脑医汇及主办方、原作者等相关权利人所有。
投稿邮箱:NAOYIHUI@163.com
未经许可,禁止进行转载、摘编、复制、裁切、录制等。经许可授权使用,亦须注明来源。欢迎转发、分享。
投稿/会议发布,请联系400-888-2526转3。





