本文转载自公众号“上海神经介入论坛”
Case Review
History
70 y/o, female.
Suffering from dizziness for half a year. Intracranial aneurysms were occasionally found.
Past medical history: coronary atherosclerotic heart disease and coronary stenting implantation.
Medication: Aspirin, Atorvastatin, Metoprolol.
NE: - .
70岁,女性。
头晕半年,检查偶然发现颅内动脉瘤。
既往史:冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病,已行冠脉支架手术。
药物:阿司匹林,阿托伐他汀,美托洛尔。
神经查体:- 。

Figure 1. MRA revealed a right anterior cerebral artery A2-3 segment aneurysm and a right middle cerebral artery bifurcation aneurysm.
图 1. MRA提示右侧大脑前动脉A2-3段动脉瘤及右侧大脑中分叉部动脉瘤。

Figure 2. HR-MR did not detect wall enhancement of the two aneurysms.
图 2. 高分辨率MRI未见右侧大脑前及大脑中动脉瘤瘤壁强化。

Figure 3 GIF. DSA confirmed a right anterior cerebral artery A2-3 segment aneurysm with a small daughter sac and a right middle cerebral artery bifurcation aneurysm involving the inferior trunk.
图 3 GIF. DSA证实右侧大脑前动脉A2-3段动脉瘤伴小子瘤,右侧大脑中分叉部动脉瘤,动脉瘤累及大脑中动脉下干。
1
Strategy
1.Both the right anterior cerebral artery A2-3 segment aneurysm with a small daughter sac and irregular right middle cerebral artery bifurcation aneurysm indicated a high rupture risk, which should be treated.
2.Advantages of a stent deployed into the callosomarginal artery:
(1)A large angle existed.
(2)The callosomarginal artery supplied a wide region and if the artery occluded, severe complications would happed.
(3)Operation will be relative safe comparing with deploying stent into the pericallosal artery.
3.Advantages of a stent deployed into the pericallosal artery:
(1)Lower the recurrence by dense packing of the aneurysm.
(2)The posterior pericallosal artery could compensated If the pericallosal artery occurred chronic occlusion.
4.Considering above, a stent will be deployed into the callosomarginal artery while the pericallosal artery will be preserved by large coils. Stent assisted large coiling technique will be adopted to lower the recurrence.
5.A stent will be deployed into the middle cerebral artery inferior trunk because the aneurysm only incorporated the large inferior trunk without an acute angle.
1.右侧大脑前A2-3段动脉瘤伴小子瘤,右侧大脑中分叉部不规则动脉瘤,破裂风险高,建议治疗。
2.大脑前动脉动脉瘤治疗时支架放在胼缘动脉的优势:
(1)角度大。
(2)胼缘动脉供血区域广泛,一旦闭塞,引起严重并发症。
(3)手术操作相对更安全。
3.支架在胼周动脉释放的优势:
(1)动脉瘤可以致密栓塞、复发风险降低。
(2)一旦胼周动脉慢性闭塞,后胼周动脉可以代偿。
4.综合考虑上述原因,决定支架放置在胼缘动脉内,用大圈代支架技术保护胼周动脉。同时采用支架辅助大圈技术降低远期复发风险。
5.由于大脑中动脉瘤只累及下干,且下干粗大,无严重成角,支架植入相对安全,所以支架放在中动脉下干内。
2
Stent assisted large coiling for an ACA AN

Figure 4. Measurements. AN size 3.6*2.6mm, AN neck 2.7mm, proximal parent artery diameter 1.8mm, distal parent artery diameter 1.8mm, pay attention to the position of the daughter sac of AN, avoid puncturing it.
图 4. 测量。动脉瘤大小3.6*2.6mm,动脉瘤颈2.7mm,近端载瘤动脉直径1.8mm,远端载瘤动脉直径1.8mm,需注意到子瘤位置,避免操作时刺破子瘤。
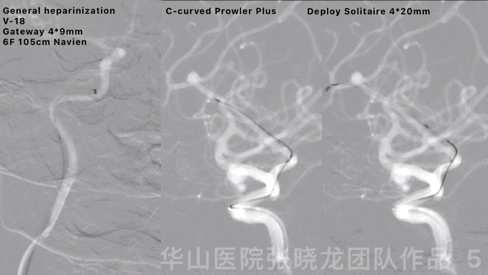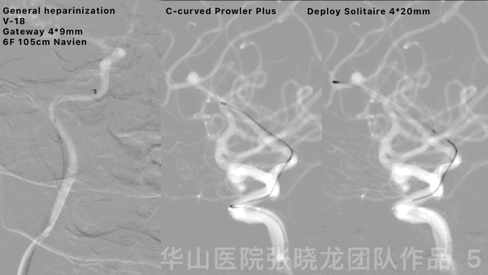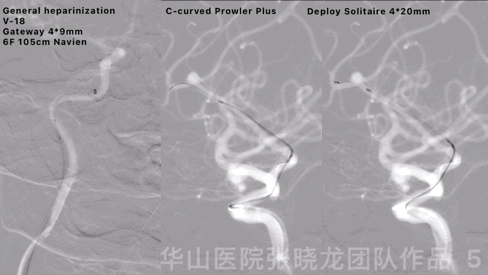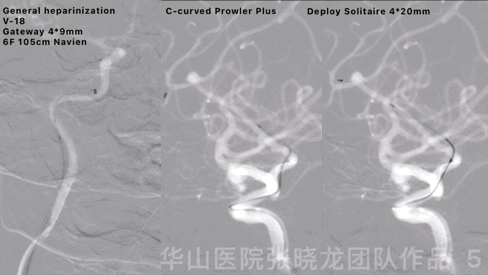
Figure 5 GIF. General heparinization was performed. 6F Navien guiding catheter was positioned to the right internal carotid artery lithogenic segment by a Gateway 4*9mm balloon and a V-18 microwire. A C-curved Prowler Plus microcatheter was navigated into the right callosomarginal artery via a Synchro II. Then deploy a Solitaire 4*20mm stent covering the aneurysm neck.
图 5 GIF. 行全身肝素化。6F Navien导引导管在Gateway 4*9mm球囊和V-18微导丝导引下置于右侧颈内动脉岩骨段。Prowler Plus微导管头端塑“C”弯后在Synchro II微导丝导引下置于右侧胼缘动脉主干内。瘤颈部释放Solitaire 4*20mm支架。

Figure 6 GIF. The stent tip was not fully opened. Made a loop of the stent microcatheter and retrieve the stent. Re-navigated and performed an angiography, no bleeding was observed.
图 6 GIF. 支架头端未完全打开,遂将支架微导管头端成襻回收支架。微导管重新超选造影,未见出血。

Figure 7 GIF. Re-deployed the stent and opened well. Angiography showed the parent artery angle a bit straightened. A Z-tipped SL-10 microcatheter was advanced into the sac.
图 7 GIF. 重新释放支架,支架打开良好。复查造影载瘤动脉成角稍增大。将SL-10微导管塑“Z”弯后置于动脉瘤腔内。

Figure 8 GIF. Insert the following three coils (Target helical soft 2D 3mm*8cm, Target helical soft 2D 2mm*4cm, Target helical soft 2D 2mm*4cm) successively. Angiography depicted the aneurysm was densely packed and no hemorrhage was observed. Tirofiban 6ml was administered.
图 8 GIF. 依次填入3枚弹簧圈(Target helical soft 2D 3mm*8cm, Target helical soft 2D 2mm*4cm, Target helical soft 2D 2mm*4cm)。复查造影,动脉瘤致密栓塞,未见出血。经导引导管给予替罗非班6ml。
3
Stent assisted large coiling for an MCA AN

Figure 9. Measurements. AN size 4.7*3.4mm, AN neck 1.7mm, proximal parent artery diameter 2.8mm, distal parent artery diameter 1.8mm.
图 9. 测量。动脉瘤大小4.7*3.4mm,动脉瘤颈1.7mm,近端载瘤动脉直径2.8mm,远端载瘤动脉直径1.8mm。

Figure 10 GIF. A C-curved Prowler Plus was navigated into the middle cerebral artery inferior trunk by the help of an acute-curved Synchro II microwire. A Z-curved Echelon-10 microcatheter was advanced into the aneurysm sac.
图 10 GIF. Prowler Plus微导管头端塑“C”弯后在Synchro II(头端塑急弯)微导丝导引下置于右侧大脑中动脉下干。Echelon-10微导管头端塑“Z”弯后置于动脉瘤腔内。

Figure 11 GIF. Deploy Solitaire 4*20mm after inserting a coil Target helical Ultra 4mm*8cm. Then continue three coils (Target helical Ultra 4mm*6cm, Target helical Ultra 3mm*8cm, Target helical Ultra 3mm*4cm).
图 11 GIF. 填入弹簧圈Target helical Ultra 4mm*8cm后瘤颈部释放Solitaire 4*20mm支架。继续填入3枚弹簧圈( Target helical Ultra 4mm*6cm, Target helical Ultra 3mm*8cm, Target helical Ultra 3mm*4cm)。
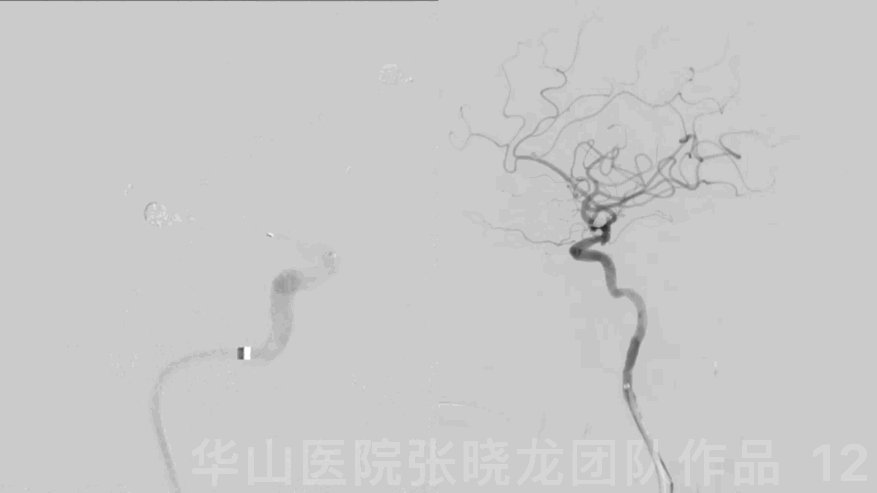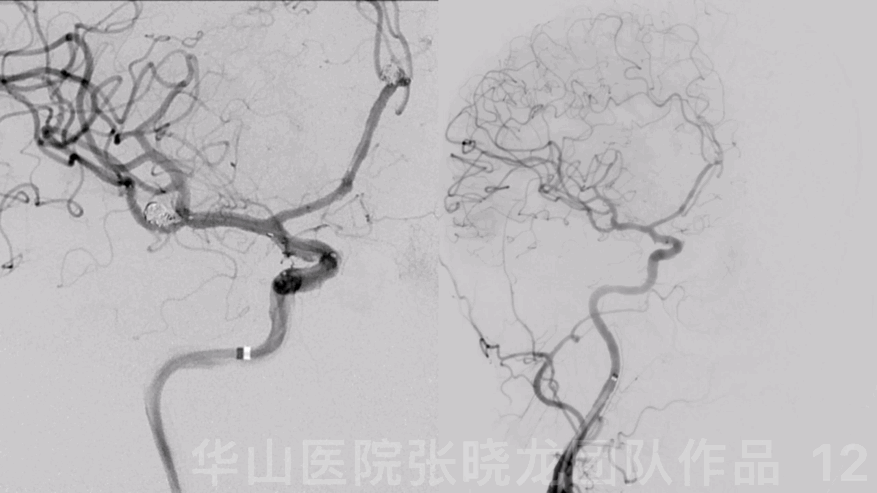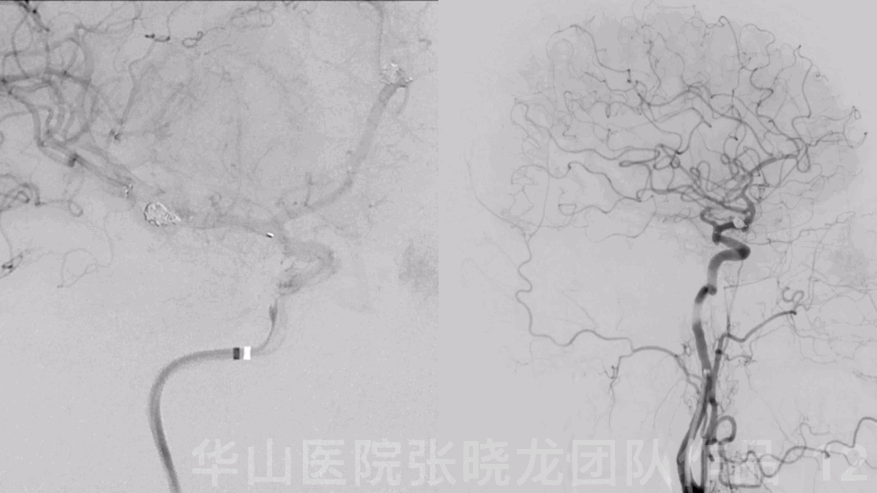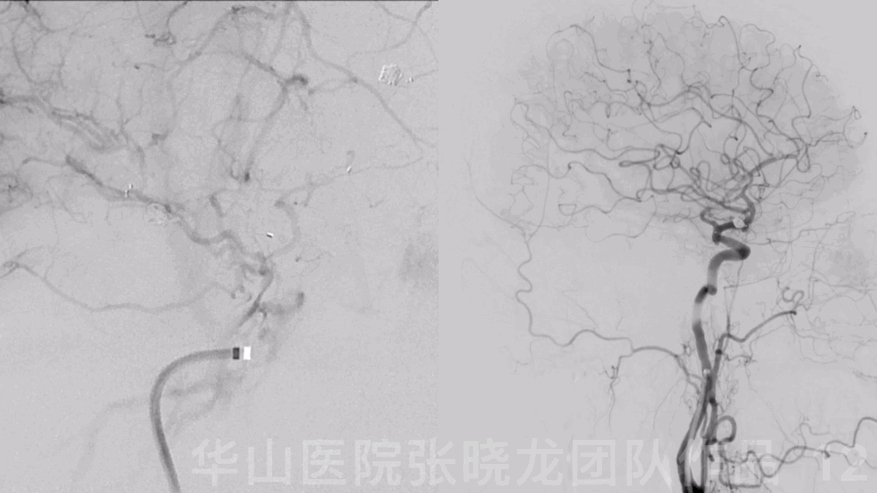
Figure 12 GIF. DSA revealed the aneurysm was densely packed and the intracranial vessels were intact.
图 12 GIF. DSA示动脉瘤致密栓塞,颅内血管显影良好。

Figure 13 GIF. Angiography showed the dense packing of the aneurysms and the parent artery patent.
图 13 GIF. 造影示动脉瘤致密栓塞,载瘤动脉通畅。
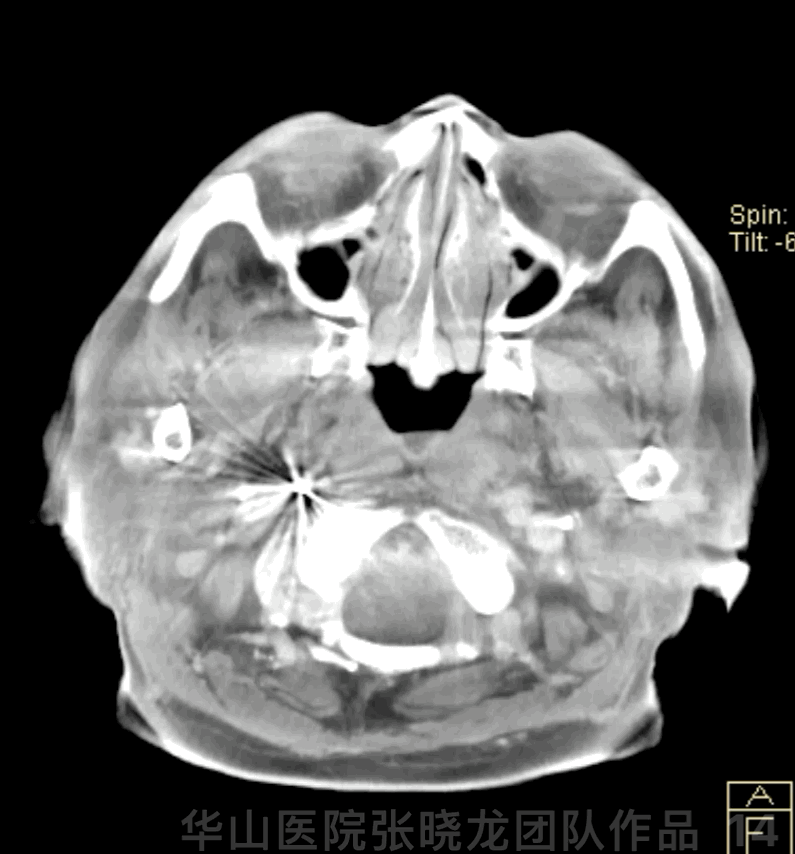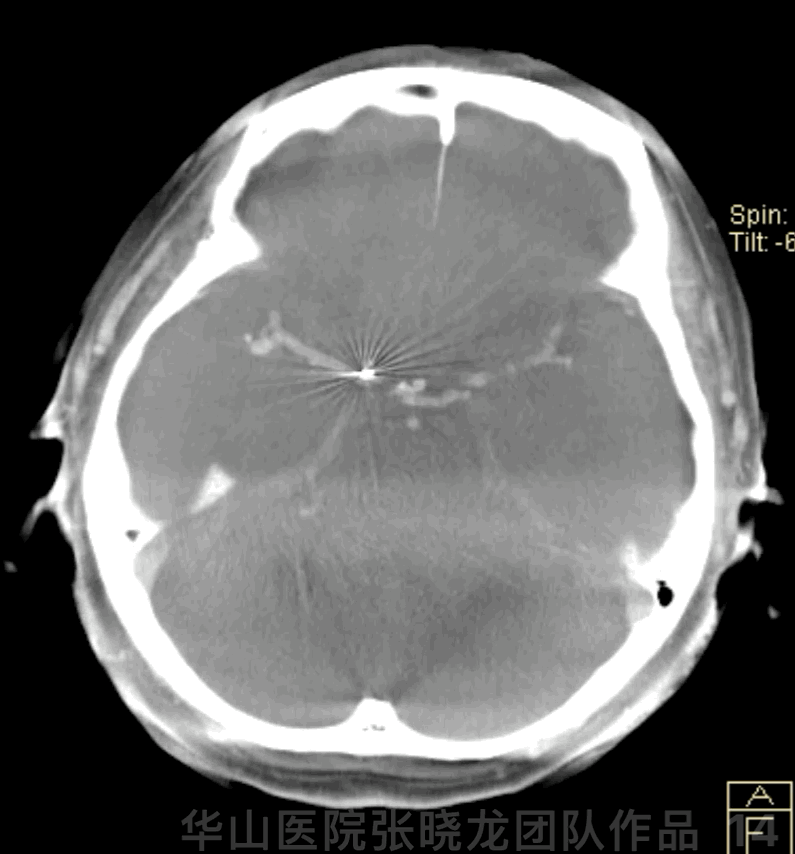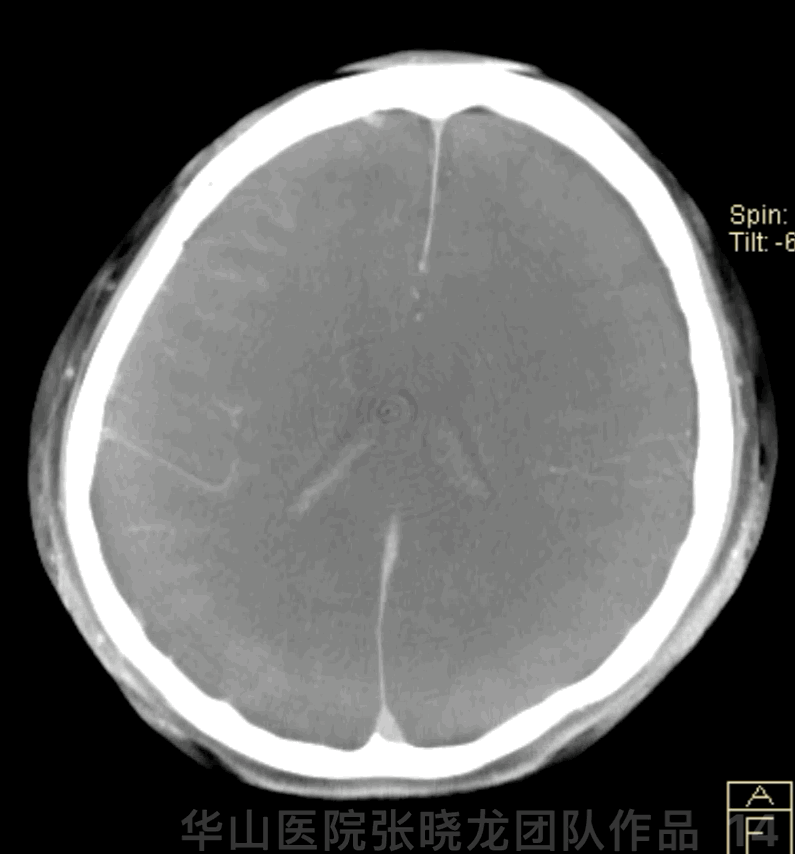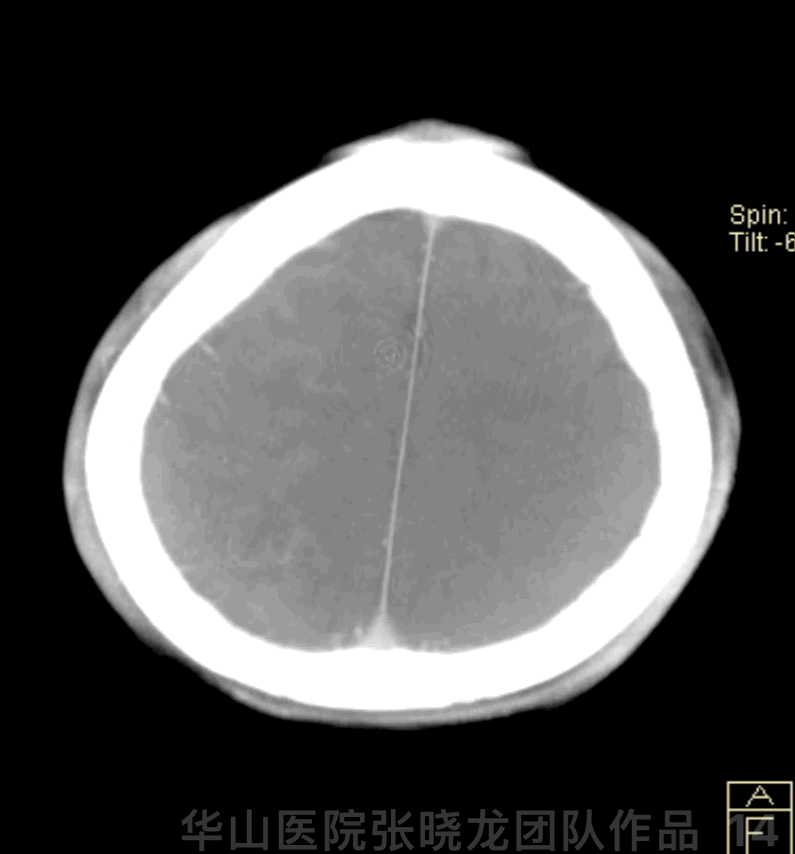
Figure 14 GIF. Dyna-CT demonstrated no hemorrhage.
图 14 GIF. 术后Dyna-CT未见出血。
4
Post-operation
Medication: Tirofiban 6ml/h maintained 48 hours. Aspirin and Clopidogrel were prescribed (AA 100%, ADP 54.8%, CYPC19 IM).
NE: GCS 15, bilateral normal muscle strength, eye movement normal, bilateral Babinski negative.
药物:替罗非班6ml/h微泵维持48h。阿司匹林及氯吡格雷口服(阿司匹林抑制率100%,氯吡格雷抑制率54.8%,氯吡格雷基因代谢中等代谢)。
查体:GCS 15,双侧肌力正常,眼球各项运动佳,双侧巴氏征阴性。
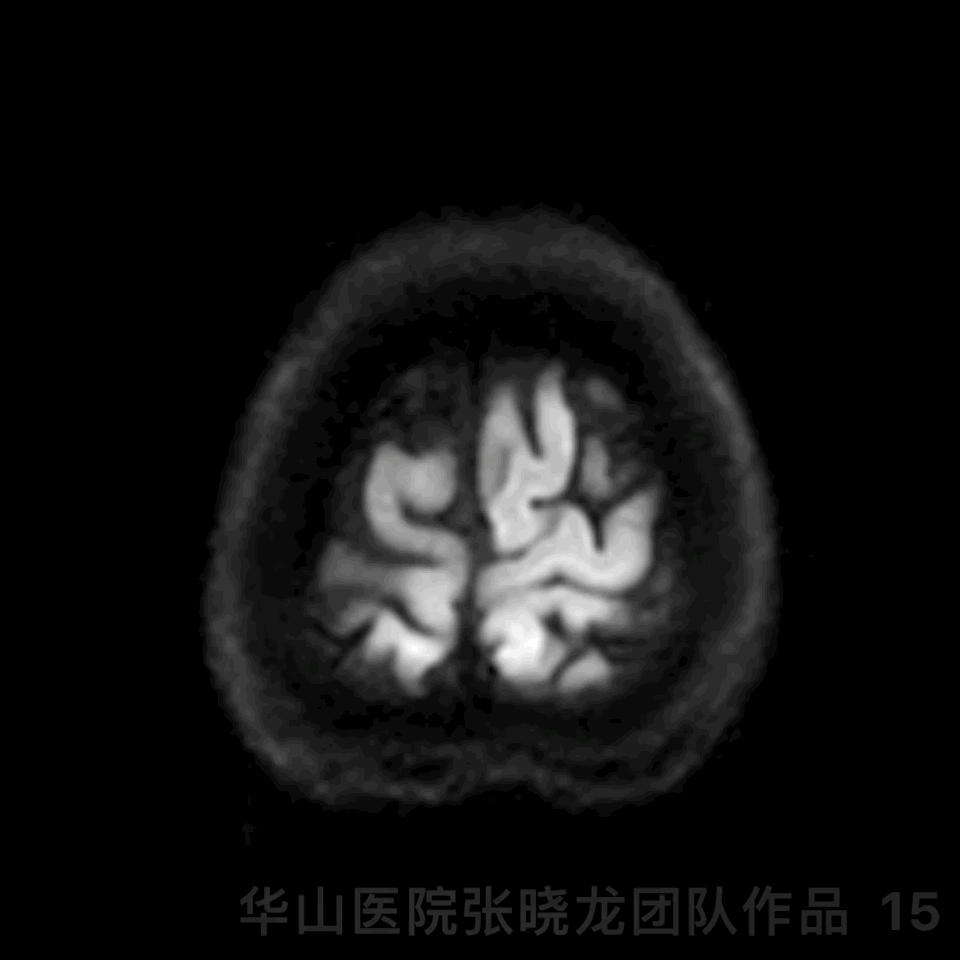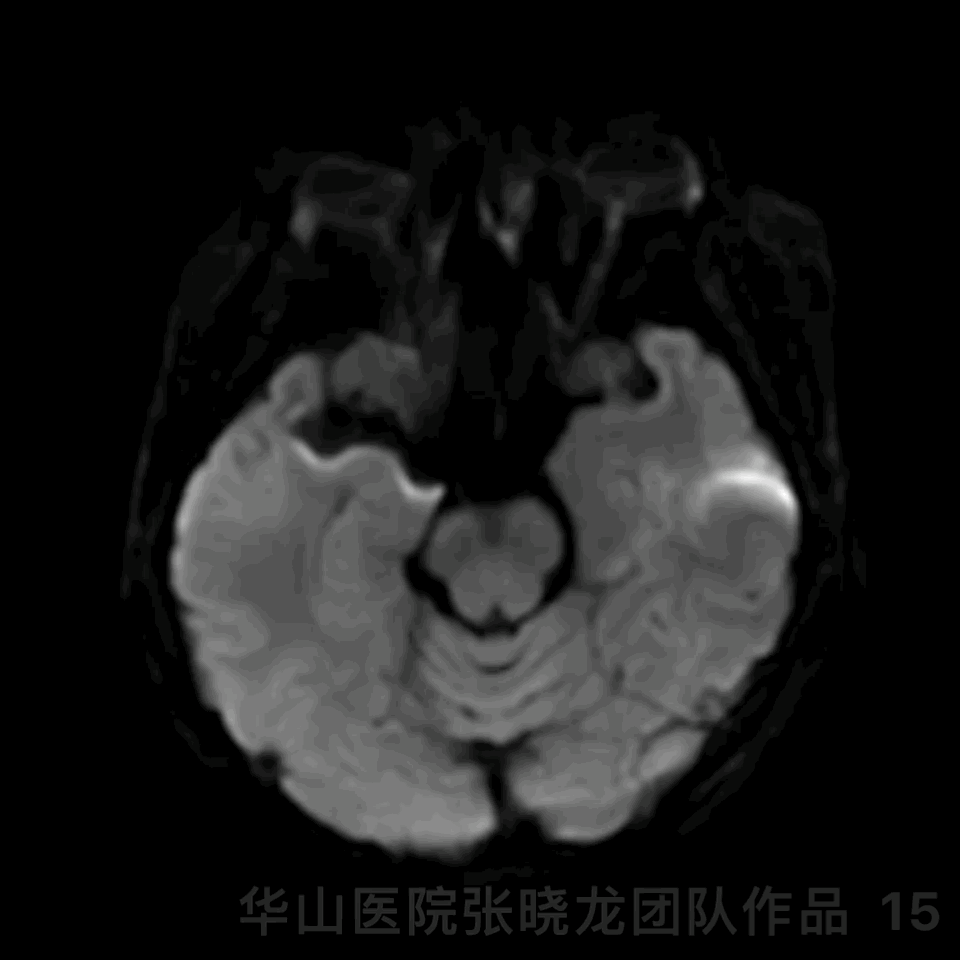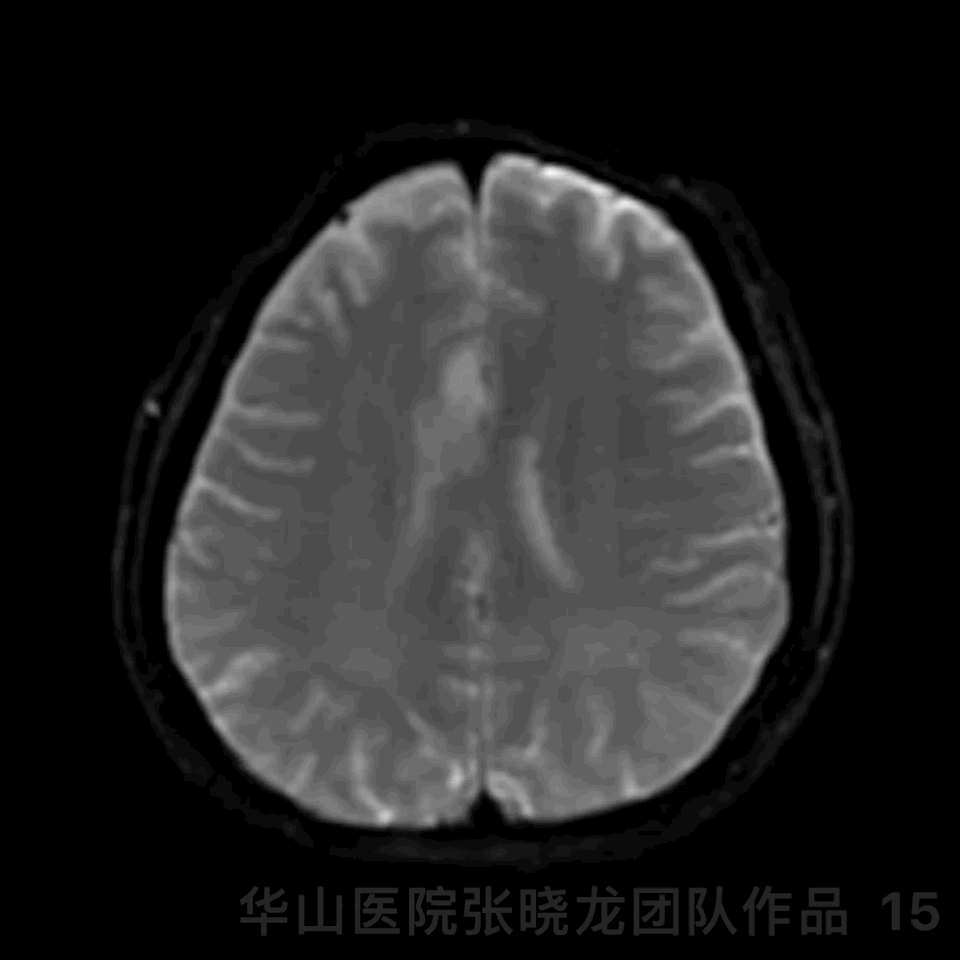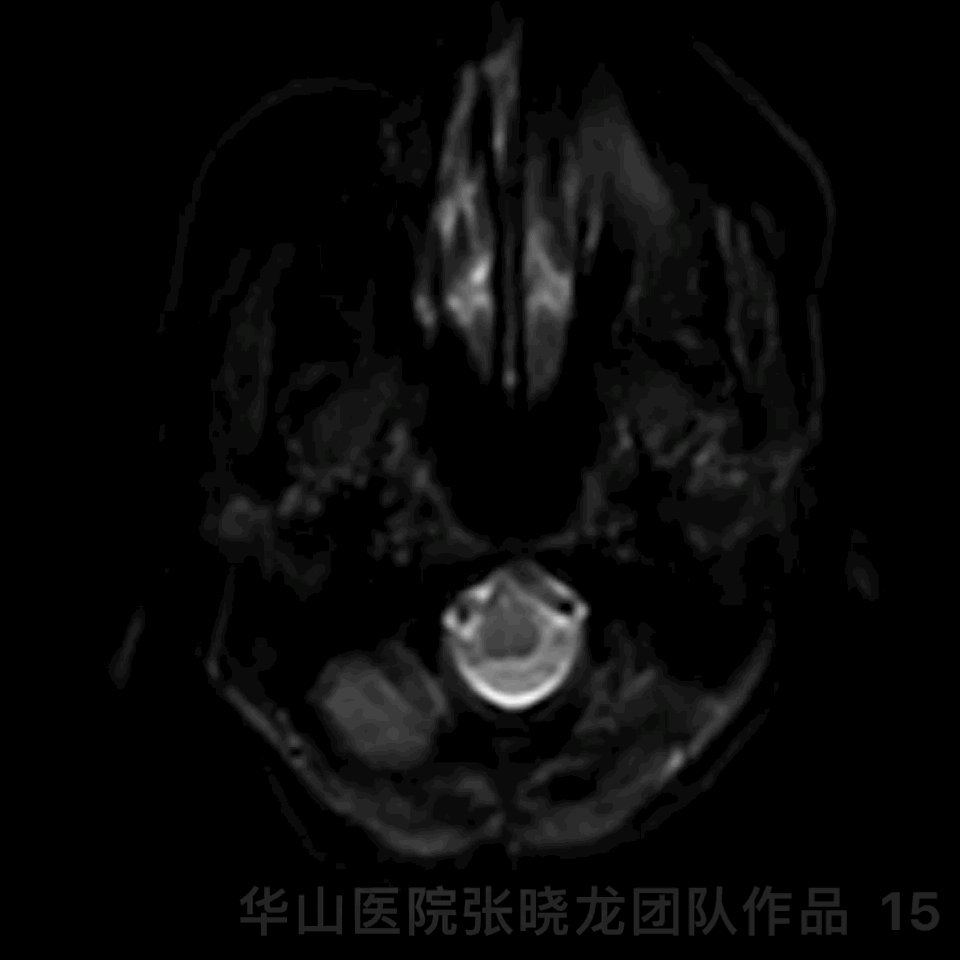
Figure 15 GIF. The patient presented with personality change. DWI revealed right callosum and right frontal lobe scattered acute infarctions. Tirofiban maintained and mannitol, glycerin fructose and butylphthalide were administered. The patient recovered post-operative day 3.
图 15 GIF. 术后患者出现性格改变。DWI提示胼胝体右侧和右侧额叶散在急性脑梗死。予替罗非班、甘露醇、甘油果糖及丁苯酞,术后第3天患者症状改善。

Figure 16 GIF. The two aneurysms were no relapsed and parent artery was patent by 11 month follow up.
图 16 GIF. 11个月随访两枚动脉瘤均未见复发,载瘤动脉通畅。

Figure 17 GIF. The parent artery angle straightened significantly.
图 17 GIF. 载瘤动脉成角明显拉直。
Video 1. Rotational DSA did not detect recurrence and parent artery patent.
视频 1. 再次复查左侧颈内动脉造影,证实无血栓形成。行Dyna-CT,未见出血。
Video 2. The intracranial vessels were intact.
视频 2. 颅内血管完好。
Summary
1.Both the right anterior cerebral artery A2-3 segment aneurysm with a small daughter sac and irregular right middle cerebral artery bifurcation aneurysm indicated a high rupture risk, which should be treated.
2.A stent was deployed into the callosomarginal artery while the pericallosal artery was preserved by large coils considering as the following reasons:
3.A large angle existed.
4.The callosomarginal artery supplied a wide region and if the artery occluded, severe complications would happed.
5.The posterior pericallosal artery could compensated the region if the pericallosal artery occluded slowly.
6.Operation was relative safe comparing with deploying stent into the pericallosal artery.
7.Stent assisted large coiling technique will be adopted to lower the recurrence.
8.A stent will be deployed into the middle cerebral artery inferior trunk because the aneurysm only incorporated the large inferior trunk without an acute angle.
9.Due to severe arteriosclerosis, the guiding should be navigated as far as possible.
10.Stents straightened a parent artery can reduce the recurrence.
11.Continue Aspirin and Metoprolol. Next follow up was scheduled in 2-3 years.
1.右侧大脑前A2-3段动脉瘤伴小子瘤,右侧大脑中分叉部不规则动脉瘤,破裂风险高,建议治疗。
2.大脑前动脉动脉瘤治疗时支架放在胼缘动脉,用大圈代支架技术保护胼周动脉,原因如下:
3.胼缘动脉成角较大。
4.胼缘动脉更粗大、供血区域广泛,一旦闭塞,引起严重并发症。
5.若胼周动脉慢性闭塞,后胼周动脉可以代偿。
6.手术操作相对更安全。
7.采用支架辅助大圈技术降低远期复发风险。
8.由于大脑中动脉瘤只累及下干,且下干粗大,无严重成角,支架植入相对安全,所以支架放在中动脉下干内。
9.由于血管粥样硬化,导引导管要尽可能上高。
10.支架拉直载瘤动脉成角能降低动脉瘤远期复发风险。
11.建议继续阿司匹林和美托洛尔口服。2-3年后再次入院复查脑血管造影。
END
张晓龙
复旦大学附属华山医院
复旦大学附属华山医院放射科主任医师,博士、教授、博士生导师;
斯坦福大学医学院客座临床教授;
主持国家自然科学基金3项,第一作者或通讯作者发表国内外权威期刊文章50余篇;
中华医学会、放射学会、卫生部医政司等组织中担任副主任委员、组长等职务.《中国名医百强榜》神经介入专业中国十强(2012年度、2013年度、2014年度、2015-16年度、2017-18年度);
擅长复杂和疑难脑血管疾病的介入治疗,如复杂脑动脉瘤的栓塞,硬脑膜动静脉瘘栓塞,脑动静脉畸形栓塞,脑梗死的支架,脊髓血管畸形治疗;
自1995年开始从事脑血管疾病介入诊治工作和研究,师从黄祥龙教授、沈天真教授和凌锋教授,是我国最早从事神经介入的专家之一。2010年9月至今连续介入治疗颅内动脉瘤1500余例,无操作致死。
点击或扫描上方二维码,
前往 张晓龙教授 学术主页
查看更多精彩内容
The End
点击或扫描上方二维码
查看更多“介入”内容







