在The Rhoton Collection解剖视频中,《Cerebellopontine Angle and Fourth Ventricle》这一章节包含了《颞骨解剖(后颅窝部分)》的内容,于是笔者将颞骨解剖(后颅窝部分)与桥小脑角区 合为一篇学习笔记,共108张图片。错误之处,请批评指正!
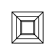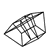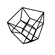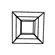
桥小脑角区
Cerebellopontine Angle
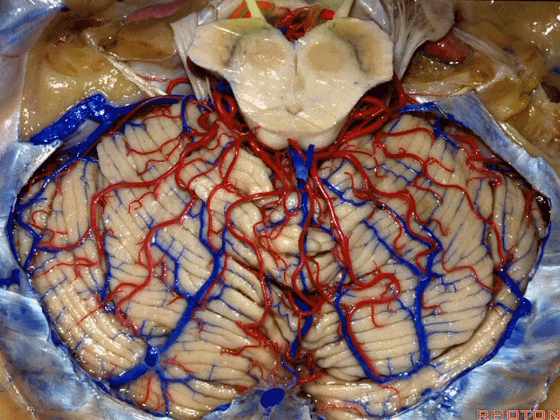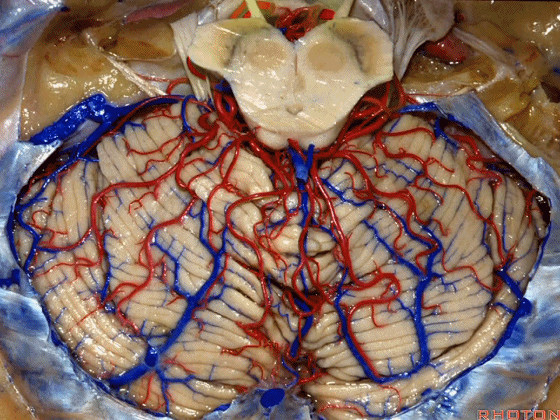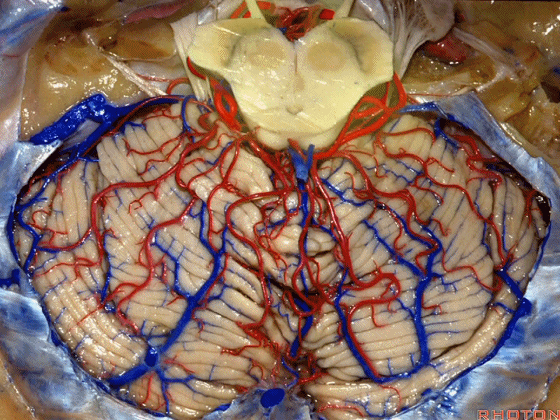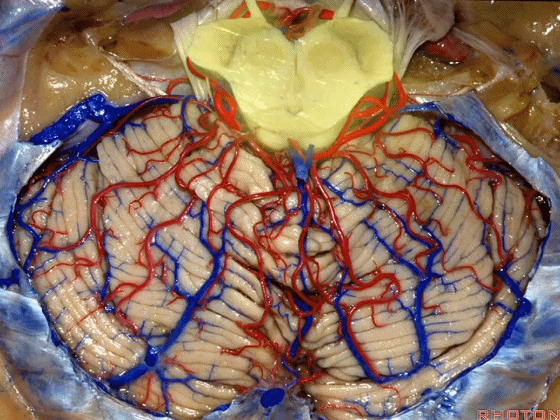
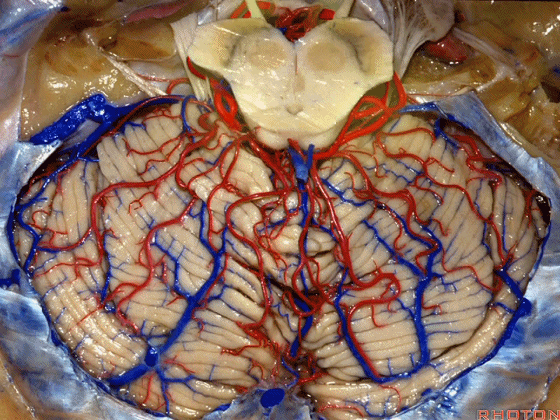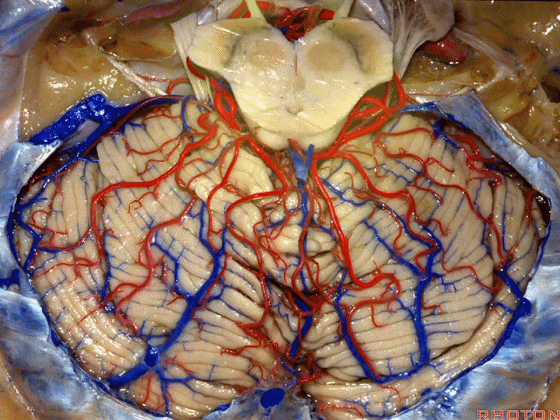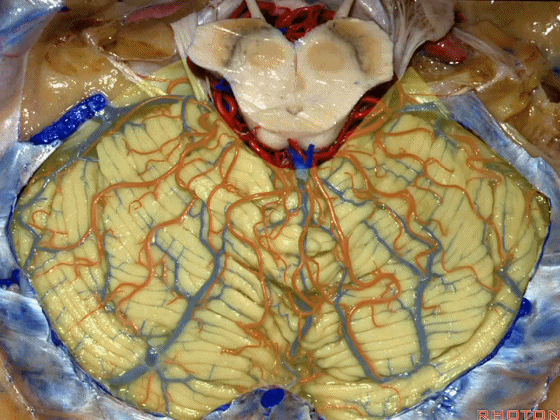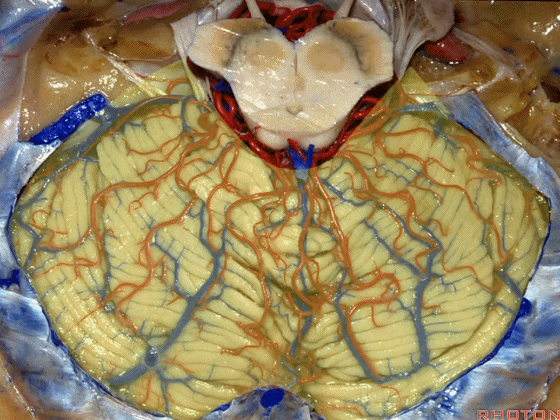
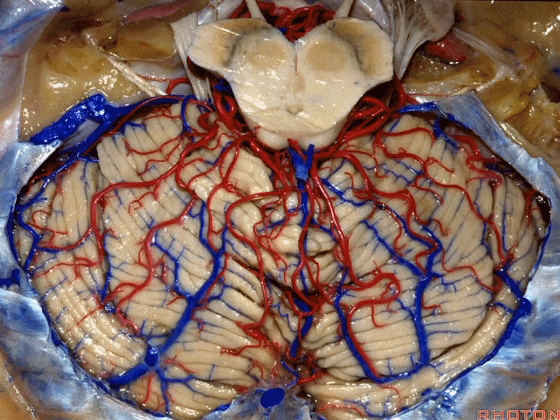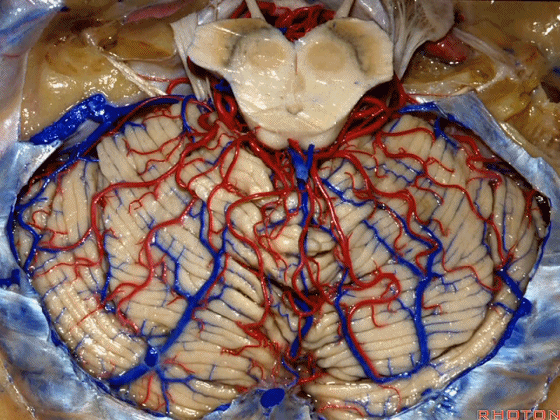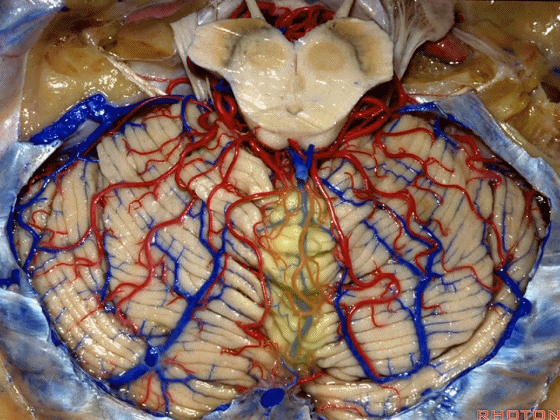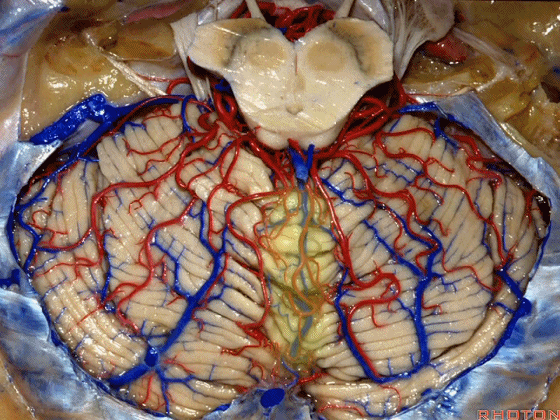
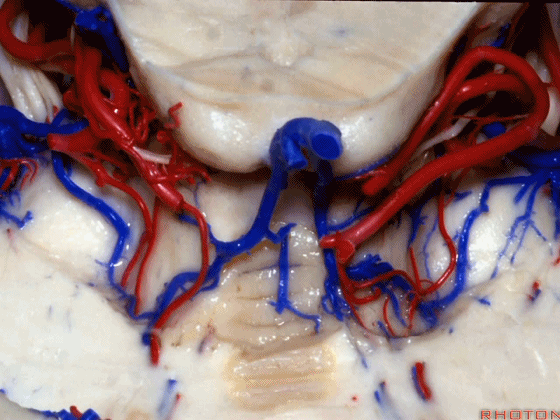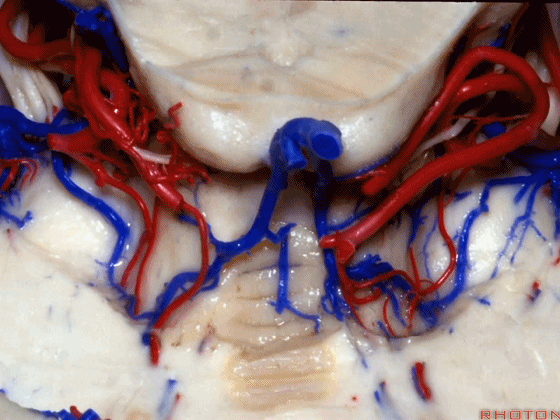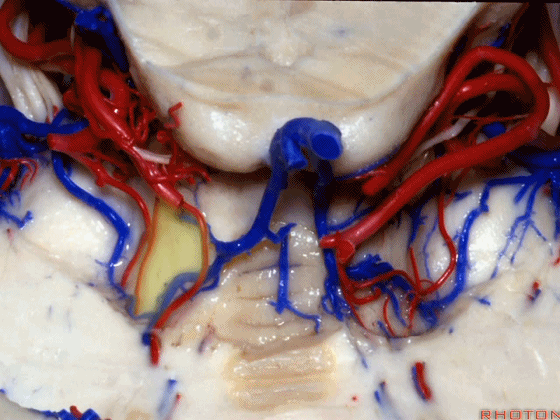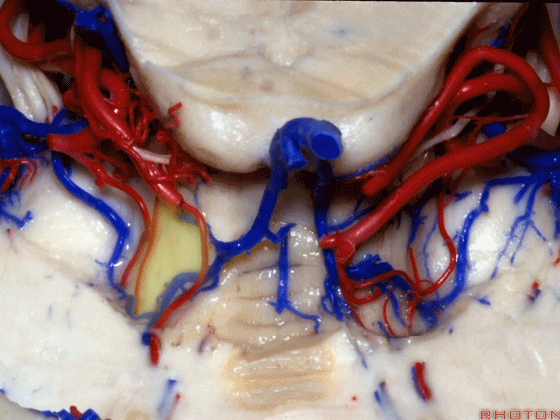
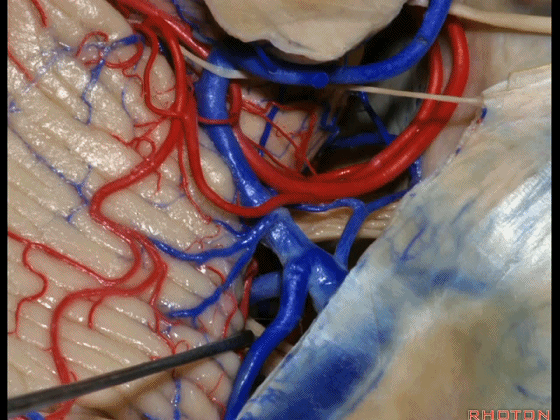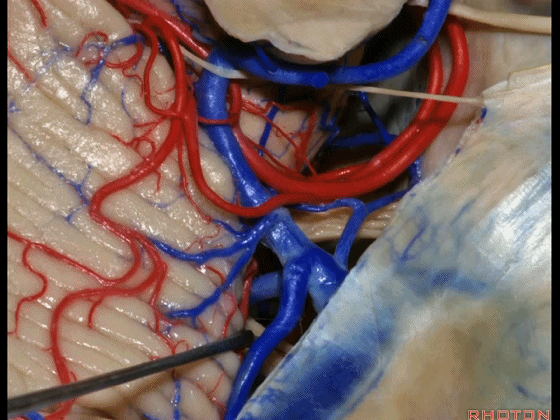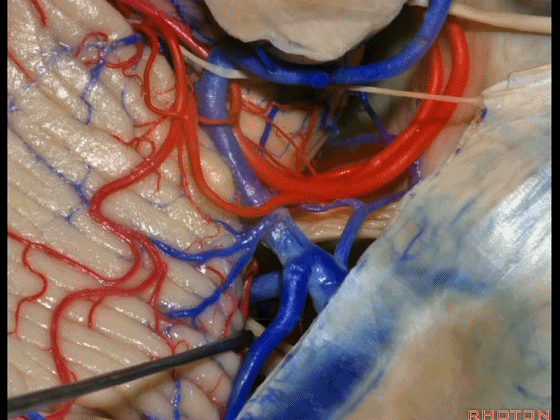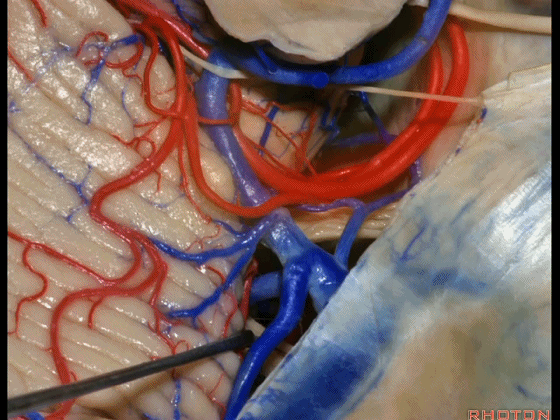
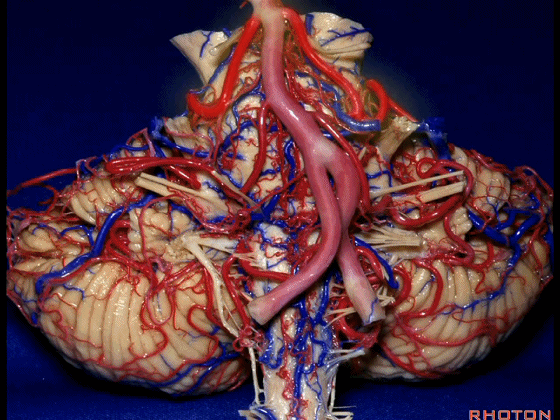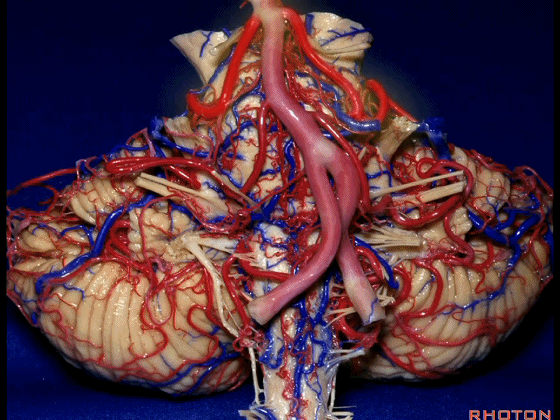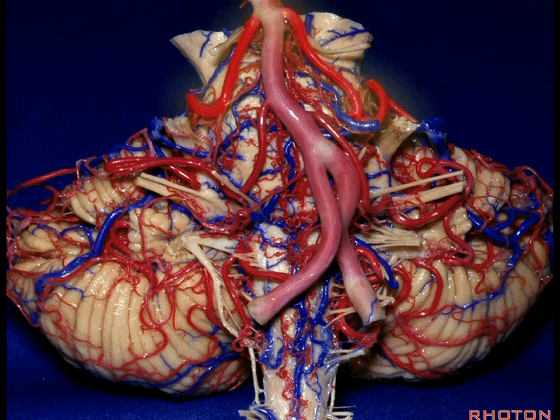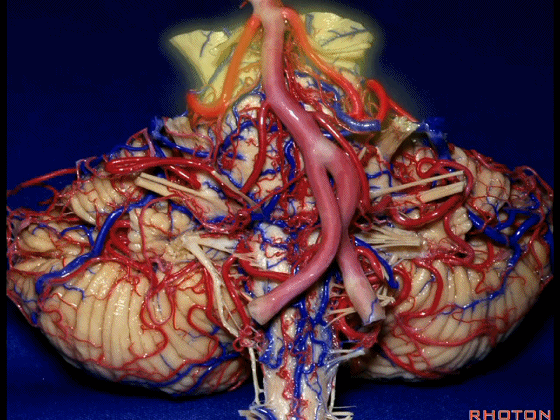
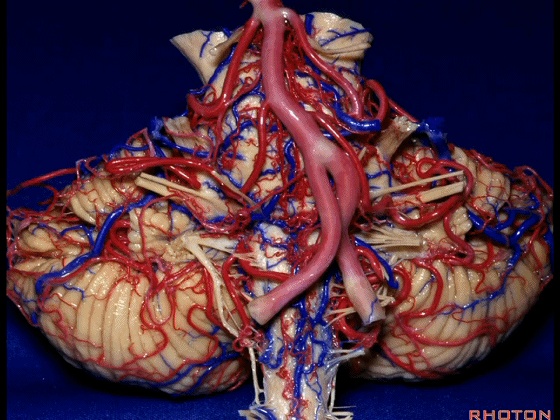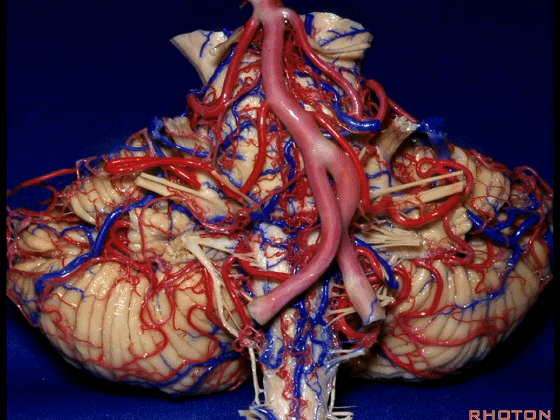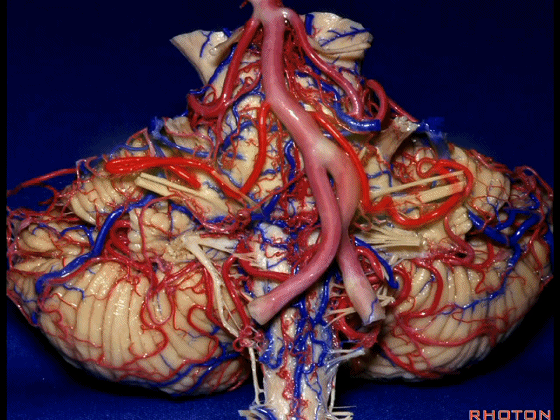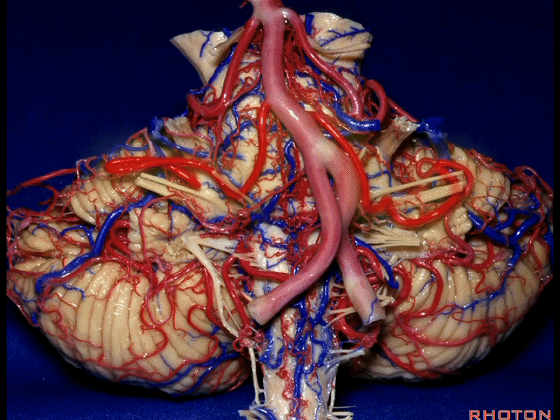
▼今天我们讲的是桥小脑角和相关颞骨的解剖,着重关注面听神经的解剖(下图)。
So we're doing CP angle and temporal bone and we're working in this area here, at VII and VIII.

▼下图这个结构是小脑绒球(flocculus ['flɒkjələs])。我曾在各种会议中问及很多医师,但是不止一位不知道我问的就是小脑绒球,而它正是桥小脑角区的一个重要解剖标志。
And this is...flocculus. I used to be able to ask thousand surgeons in the meeting what that was and...not a single person who look in the CP angle dozens of times really look at the flocculus, but it's an important landmark in CP angle.
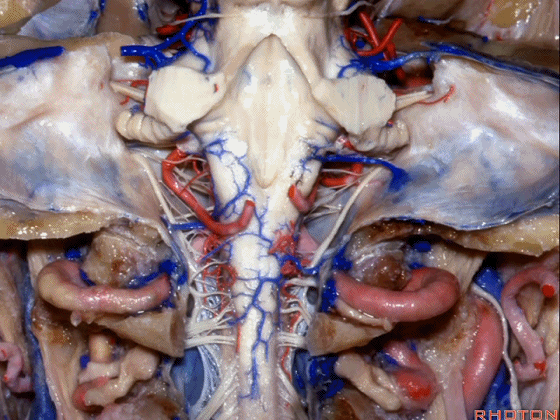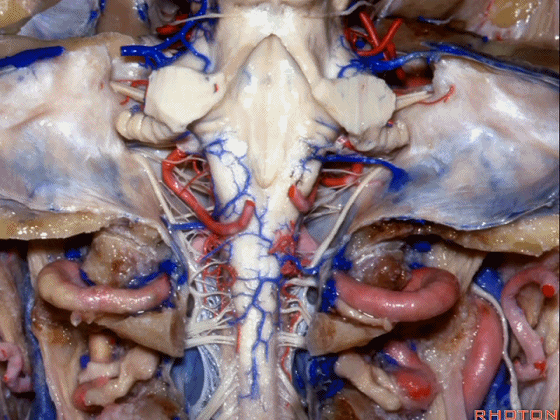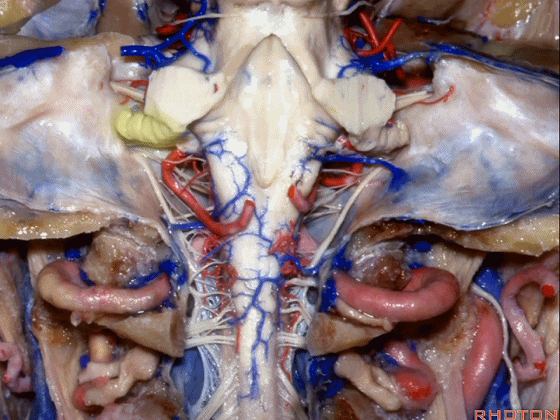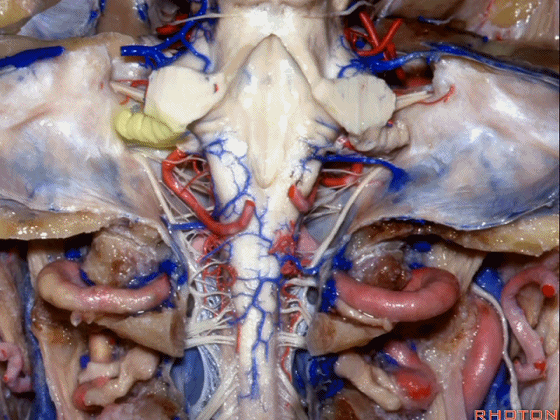
▼今天要说的神经血管复合体涉及三对重要血管:小脑上动脉、小脑前下动脉、小脑后下动脉。
下图示小脑上动脉 SCA
And we build this complex three arteries:SCA, AICA, PICA.
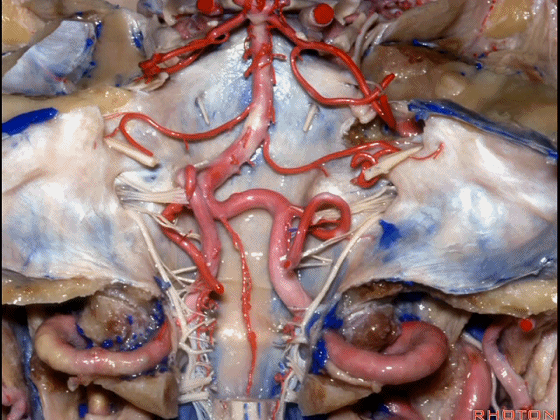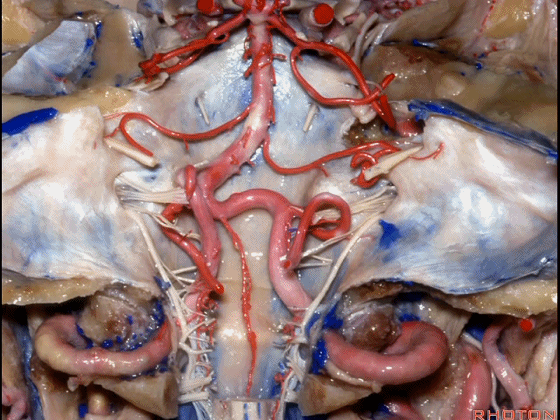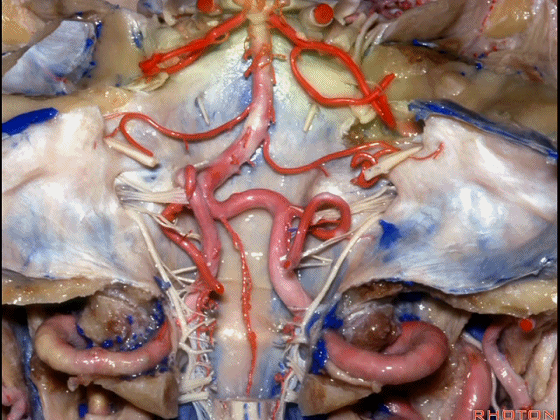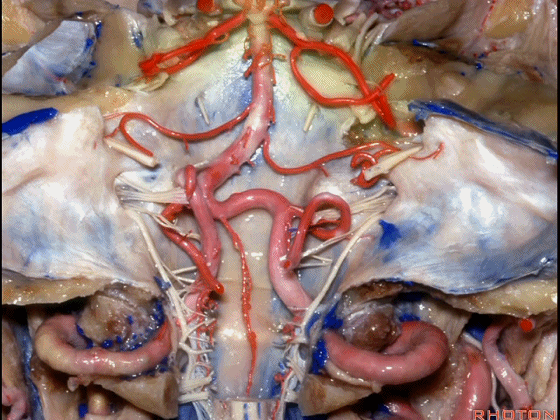
▼下图示 小脑前下动脉 AICA
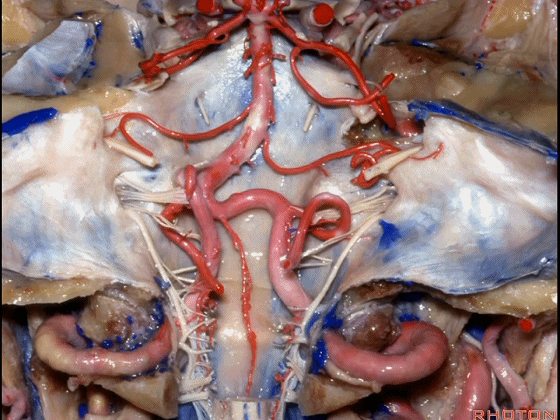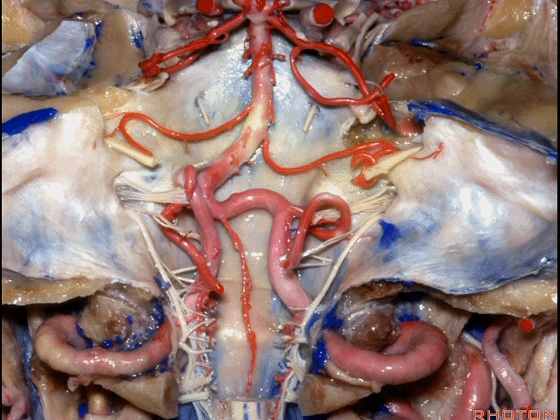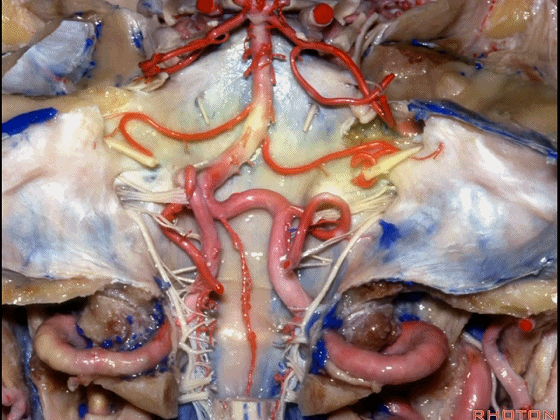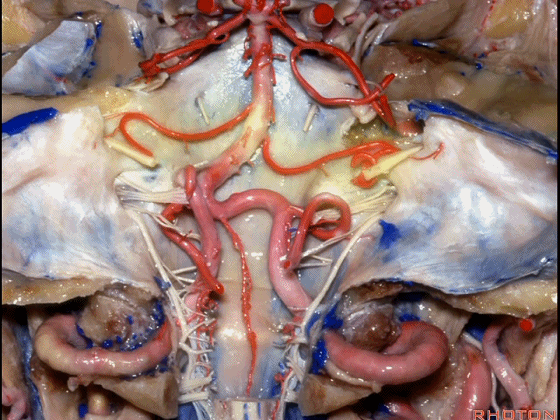
▼下图示 小脑后下动脉 PICA
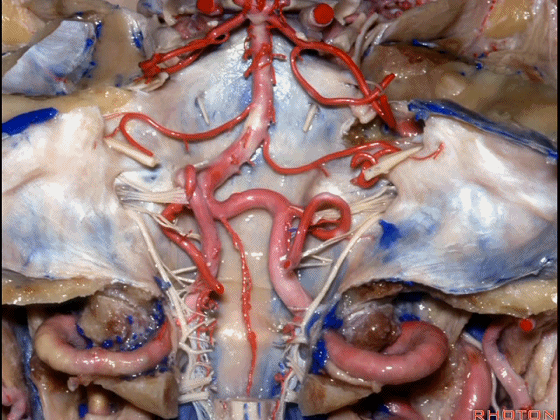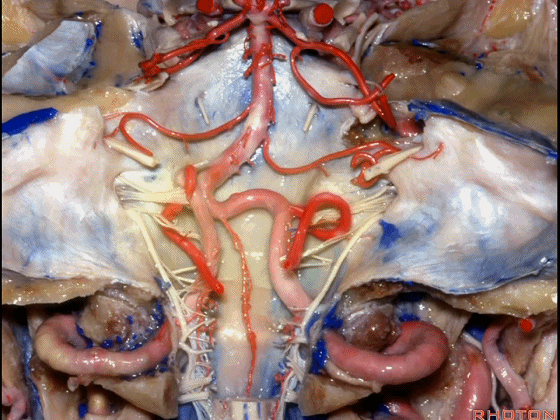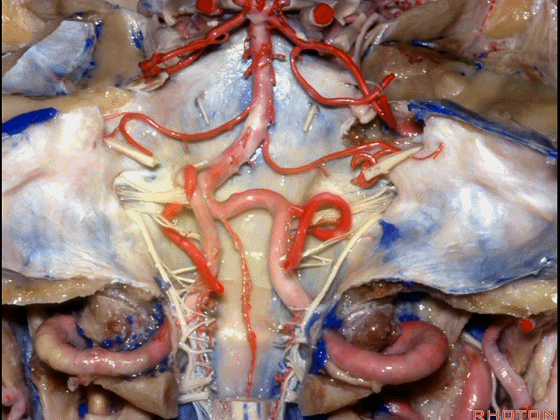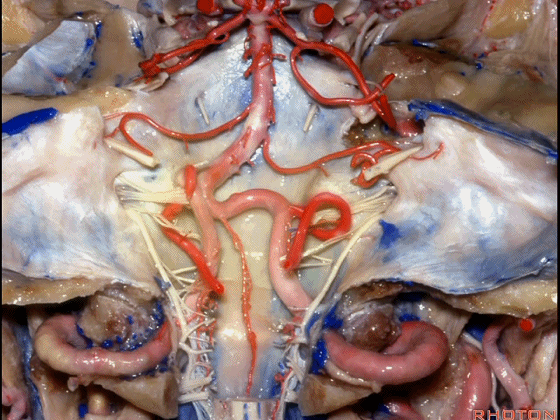
▼让我们翻开骨瓣,看一下乙状窦后入路的相关解剖。这是横窦(transverse sigmoid sinus 下图)
And we talked about that bone flap that we turn and here's transverse sigmoid sinus.
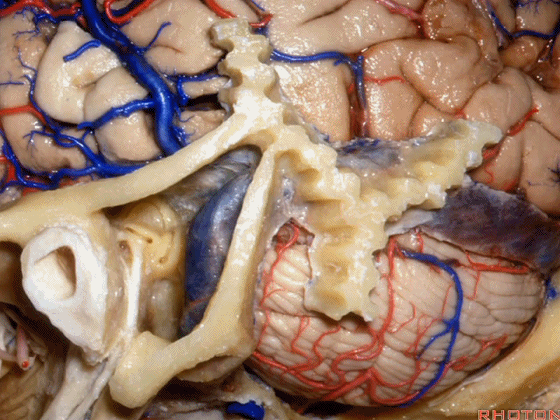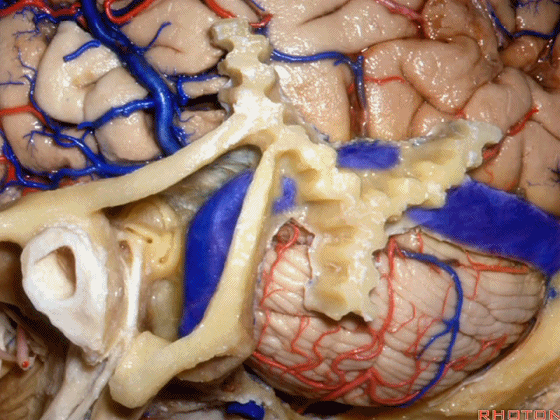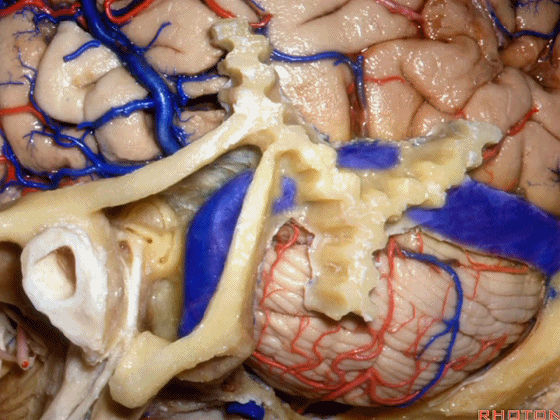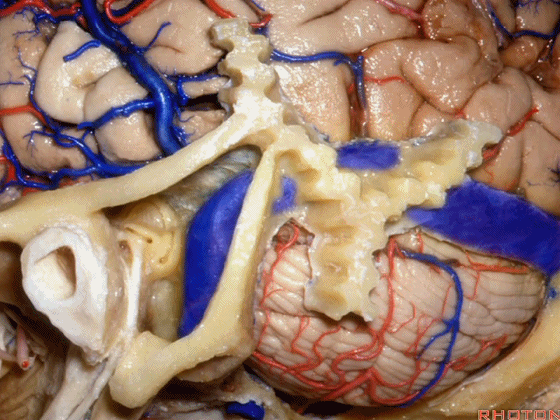
▼这是星点(asterion [æs'tern]),它一般位于横窦和乙状窦交界处(下图)的浅面,通常是交界处的下半部。
Here's the asterion right here, and it usually sits over the junction of the transverse and sigmoid, usually over the lower half of that junction.
▼术中钻孔点通常稍靠内下方,通常位于枕乳缝的后方,枕乳缝(下图)从上向下走行于乙状窦下方。
And the bur hole that we make is usually just a little medial and below, just behind the occipitomastoid suture that runs down and then eventually crosses below the sigmoid sinus.
▼现在来看上神经血管复合体。小脑上动脉 环绕 中脑
So this is upper complex, SCA encircling midbrain.
▼小脑上动脉 深入 小脑中脑裂 (cerebello-midbrain fissure 下图)之中。
It dips into this fissure
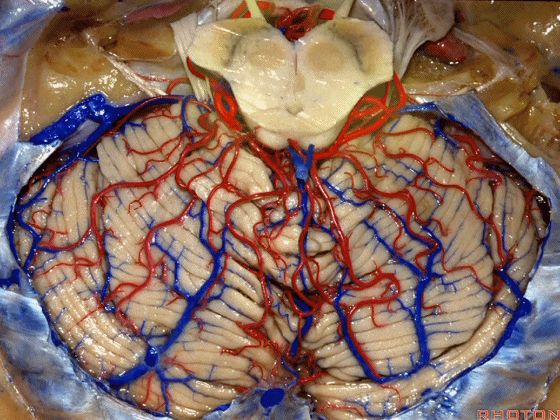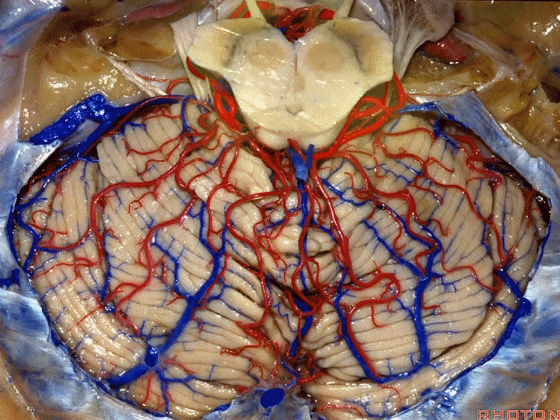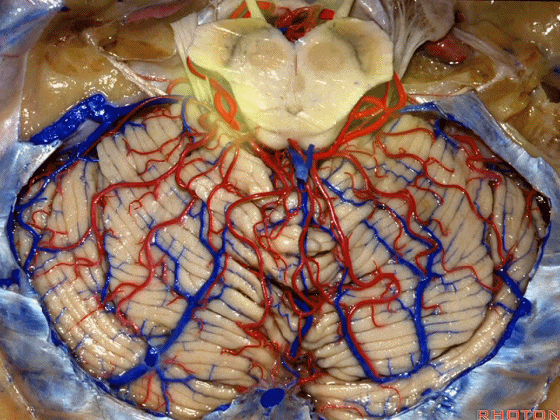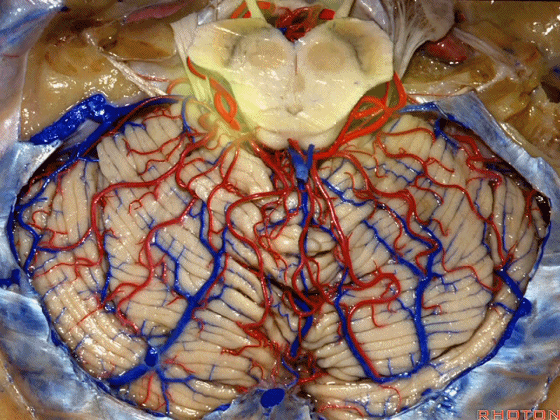
▼小脑上动脉 主要供应 小脑半球的小脑幕面
and supplies this tent shaped surface
▼小脑半球的小脑幕面最上部是 上蚓部
that has the vermis at the upper side of it.
▼这些小脑上动脉的分支,穿行在小脑中脑裂中
And these arteries as they come around the SCA, they dip into the the cerebello-midbrain fissure,
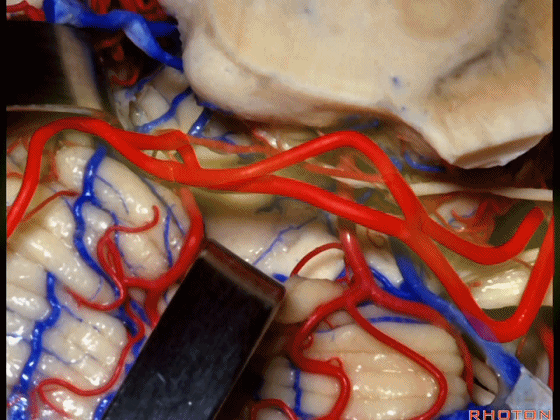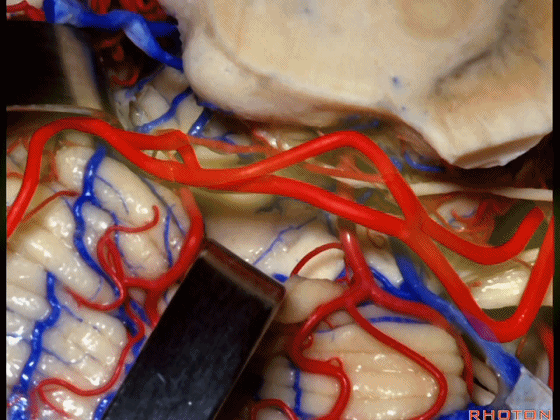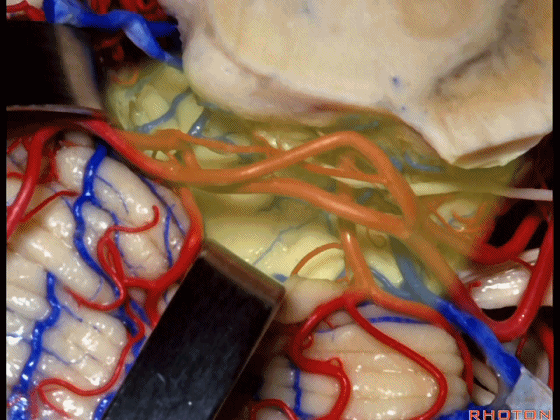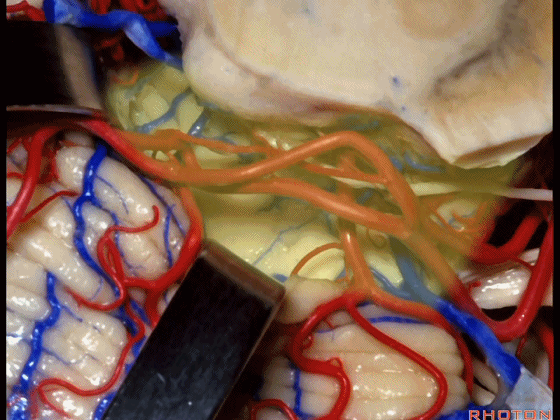
▼这些小脑上动脉的分支在小脑中脑裂内呈现一系列发卡样转弯,并与滑车神经(下图)相互缠绕。
where it has a series of hairpin turns. It's intertwined with the 4th nerve.
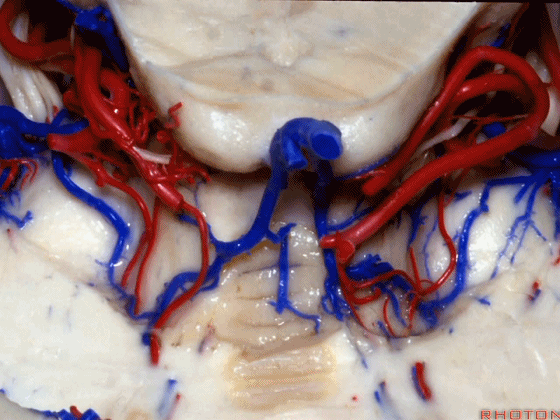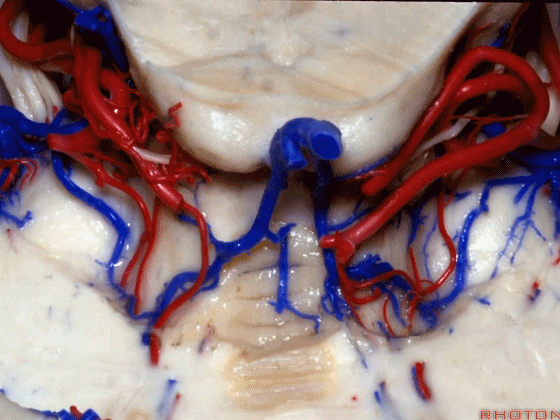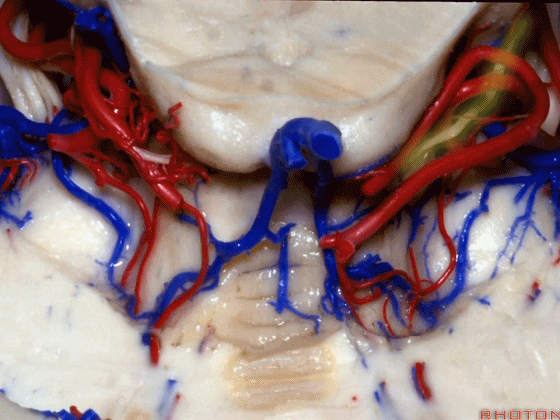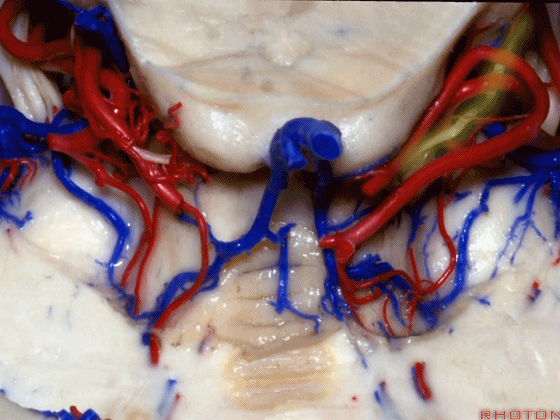
▼随后其向下发出分支供应小脑上脚(下图),以及齿状核,后者是小脑出血的最常见部位。
And then it sends its branches down the superior peduncle, then to the dental nucleus, the most common site of cerebellar hemorrhage.
▼小脑上动脉自中脑水平发出
The SCA arises at midbrain level,
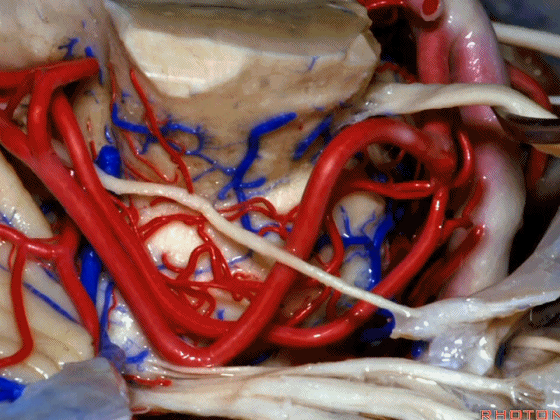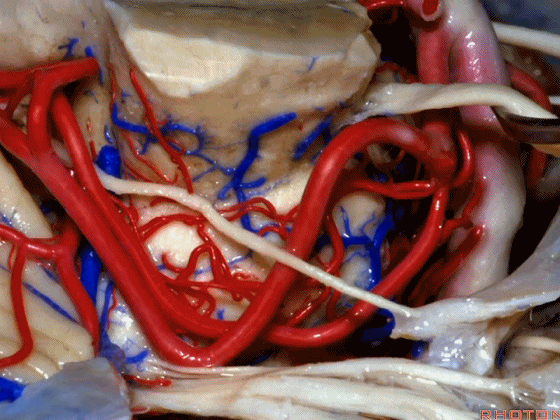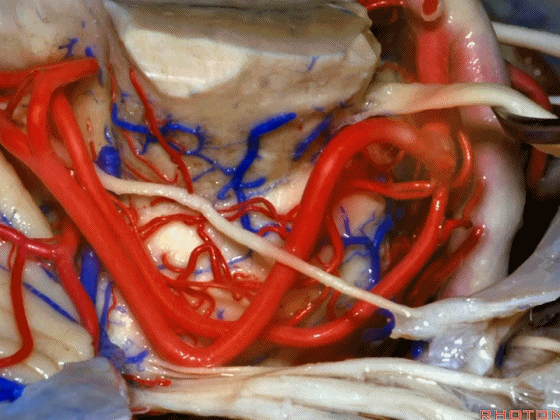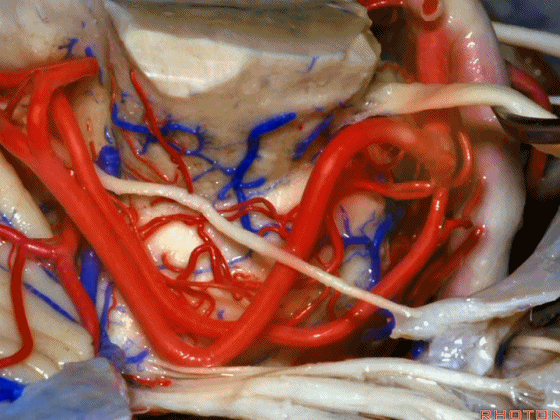
▼小脑上动脉走行在 动眼神经和滑车神经下方,三叉神经上方。
it passes below III and IV, above V.
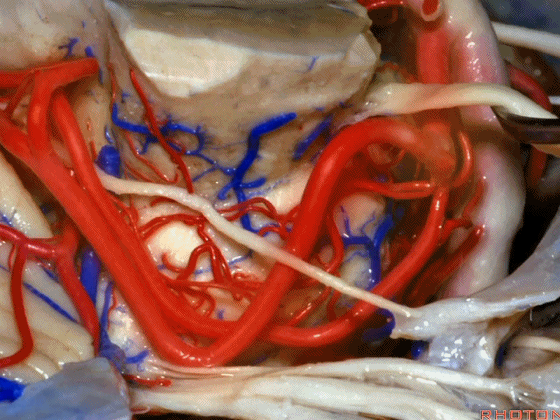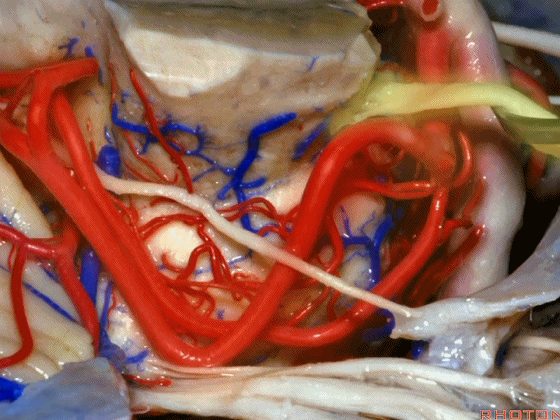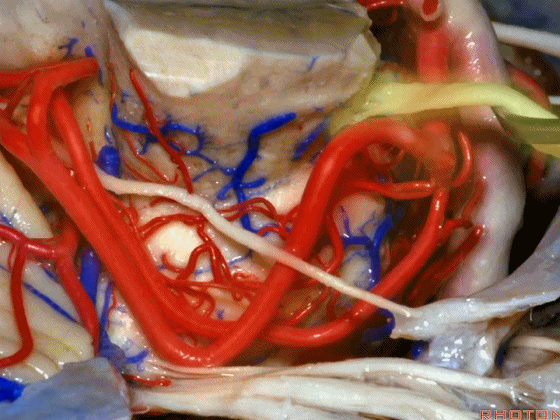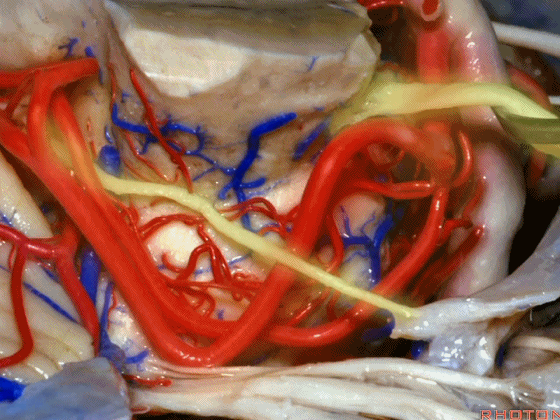
▼随着年龄的增长小脑上动脉常常向下迂曲。其通常以单一主干起源,随后分为两支,头干(下图)通向蚓部,尾干供应小脑半球幕面。
And with age it often loops downward. It arises usually as a main trunk that divides into a rostral trunk to the vermis, a caudal trunk to the hemisphere.
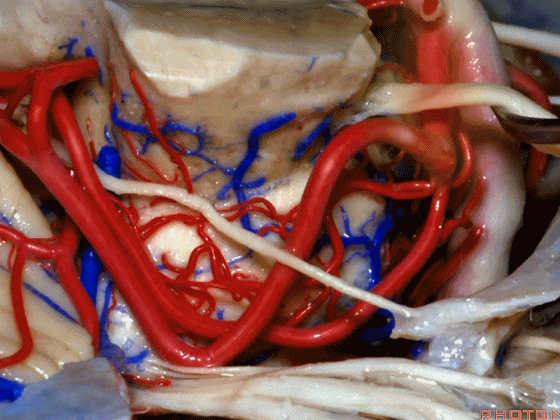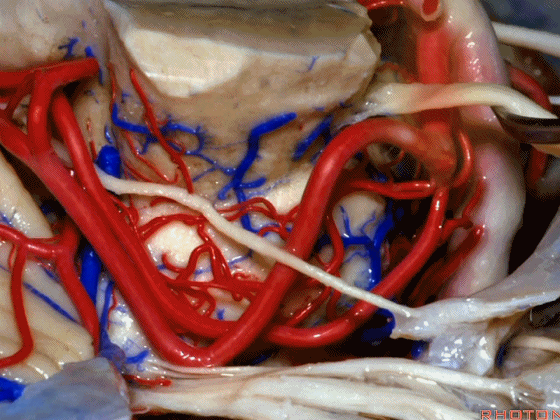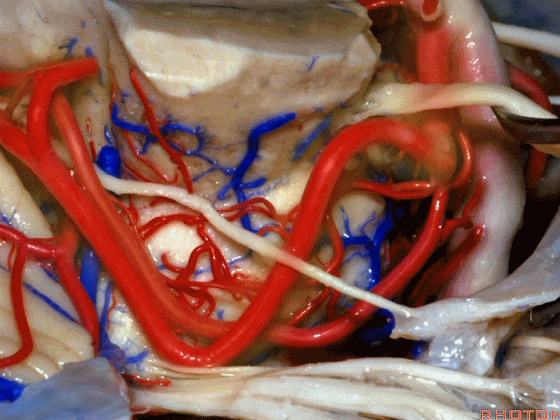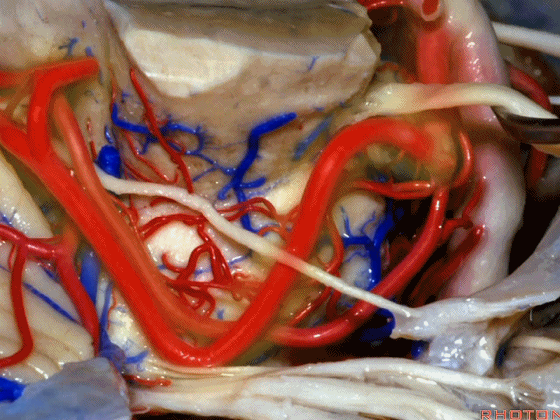
▼下图示 小脑上动脉 尾干, 供应小脑半球小脑幕面
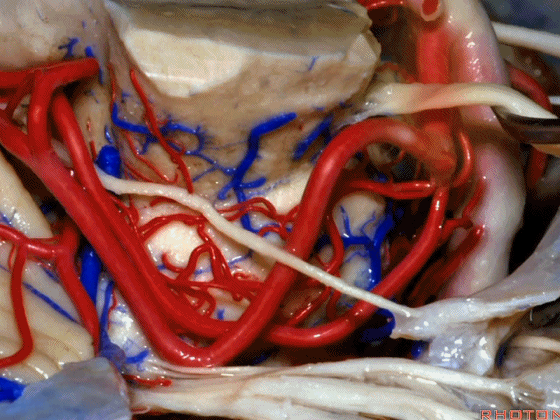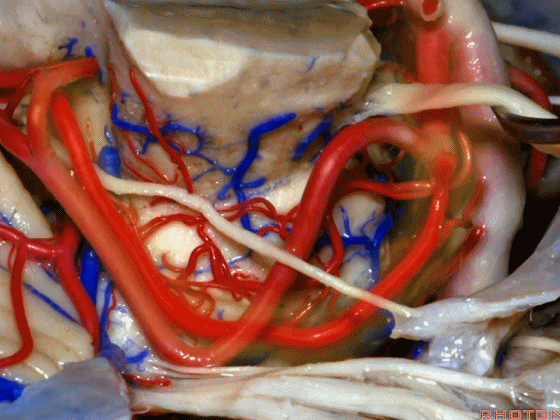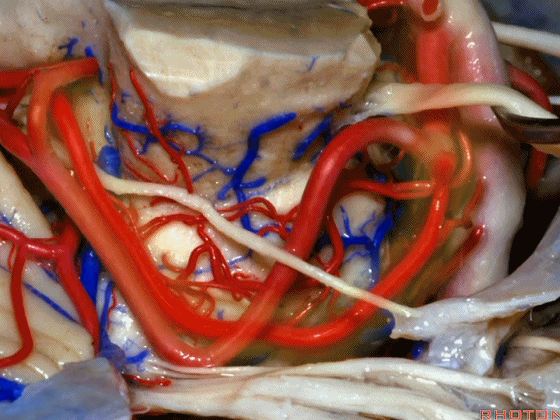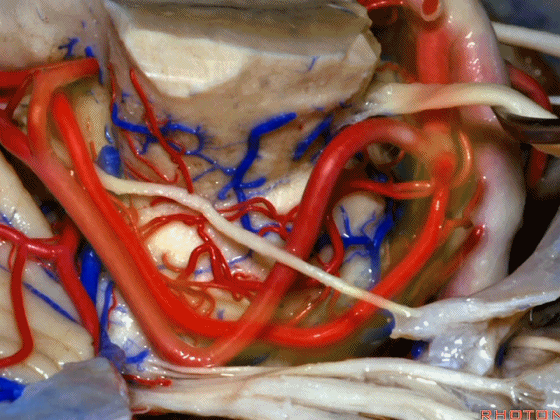
▼这些动脉干都有可能在脑干旁压迫三叉神经。而这正是三叉神经痛微血管减压术中最常见的情况。
And any of these trunks can comspanss the trigeminal nerve here right adjacent to brainstem. And that's the most common finding in the vascular decomspanssion operation for trigeminal neuralgia.
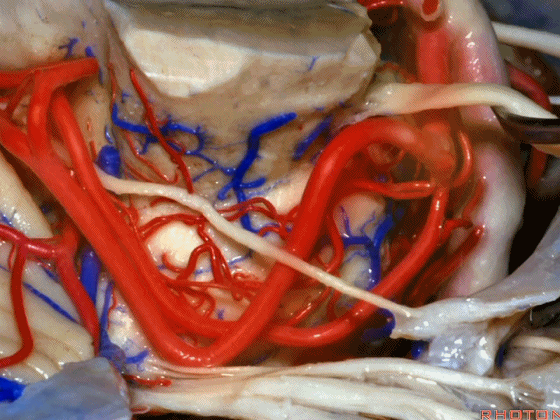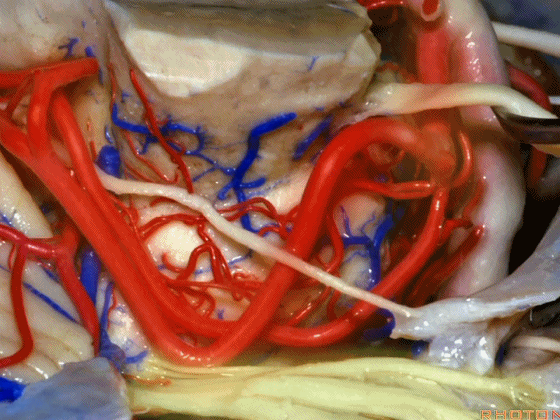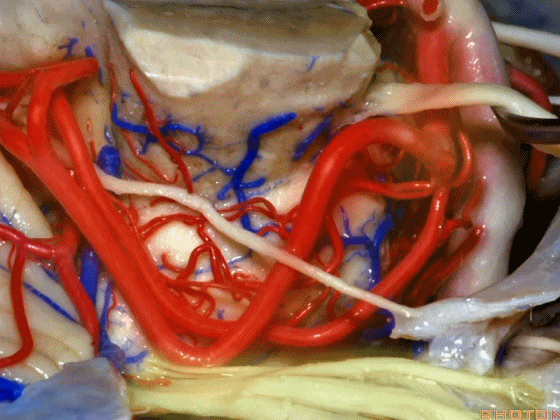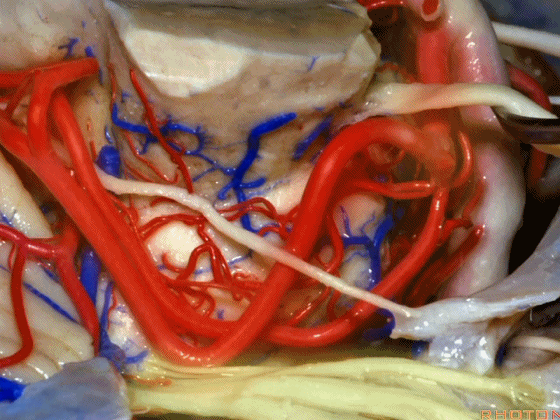
▼术中有时会牺牲这些岩上静脉或其属支,以暴露三叉神经
And when you sacrifice these superior petrosal veins or the tributaries, to get to the trigeminal nerve,
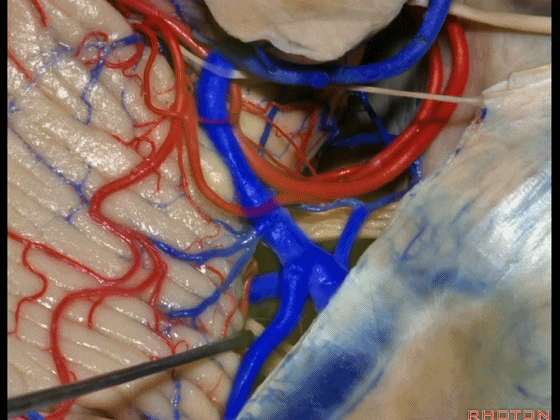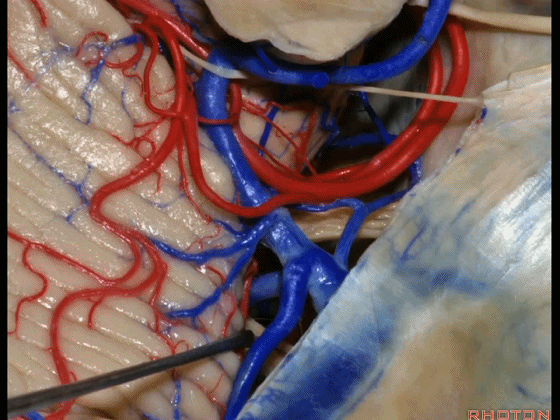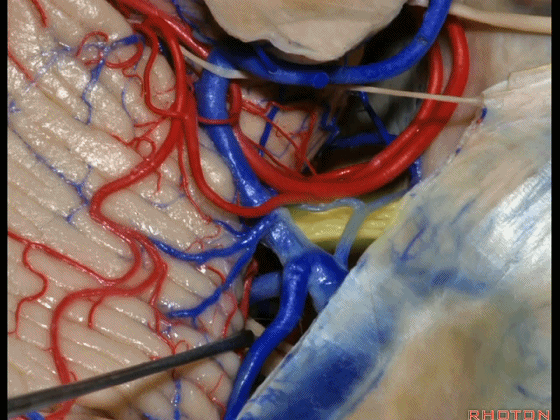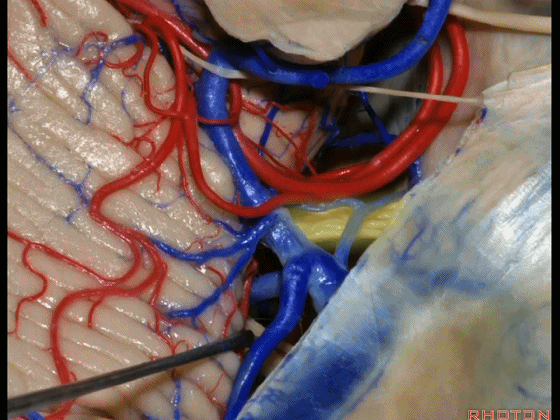
▼因此在幕下侧方入路中,接近岩上窦(下图)时,需非常小心地分离出每一支小脑上动脉的分支,它们会在蛛网膜下腔中,与静脉相粘连缠绕。
when you do the lateral infratentorial approach coming adjacent to superior petrosal sinus, always be careful to dissect out any trunks of superior cerebellar artery that may be involved in the arachnid, binding the artery to the veins.
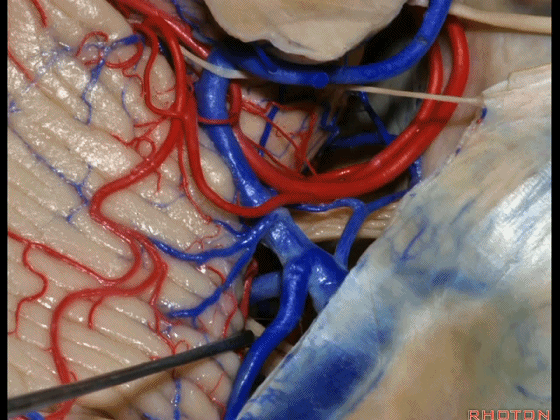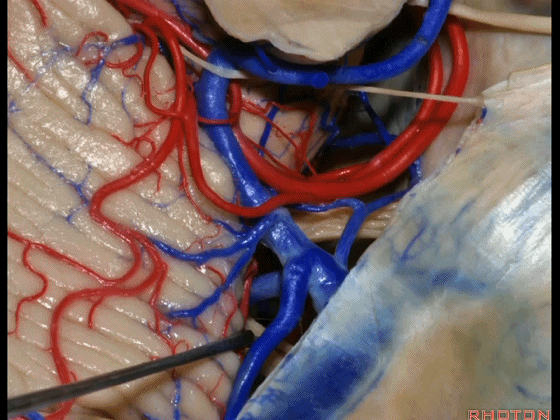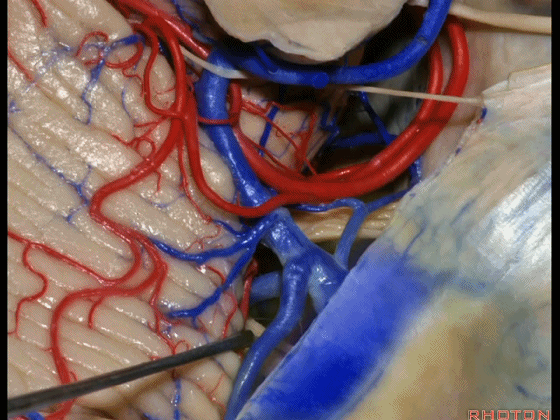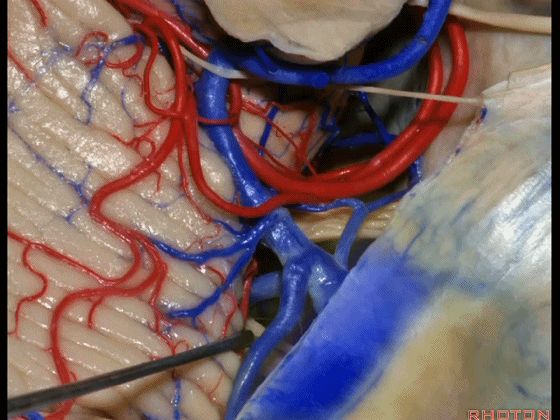
▼许多术后发生梗塞的病例往往被考虑为损伤静脉引起的静脉性梗塞,而我认为其实是损伤了小脑上动脉的分支引起的动脉性梗塞。因此在处理这些静脉时仔细操作。
I think a number of cases that are called venous infarction from taking the veins are actually arterial infarction from taking a trunk of the SCA. So be very careful in sacrificing these veins.
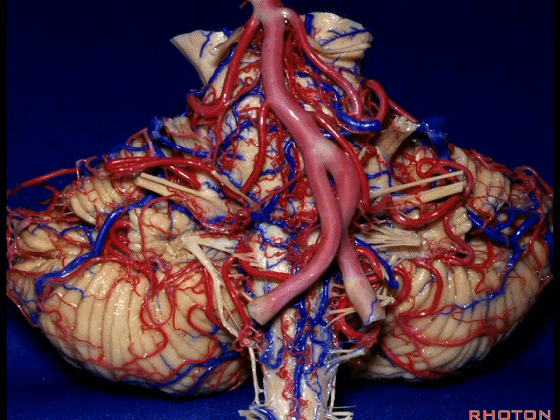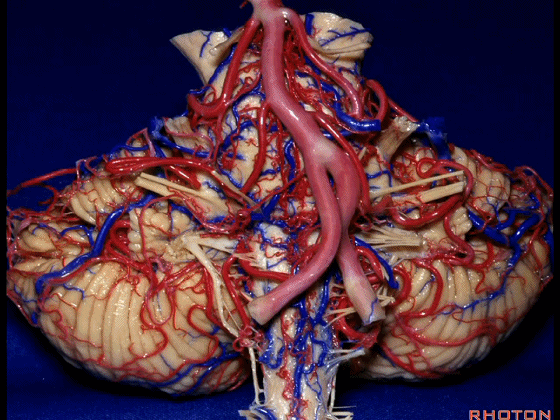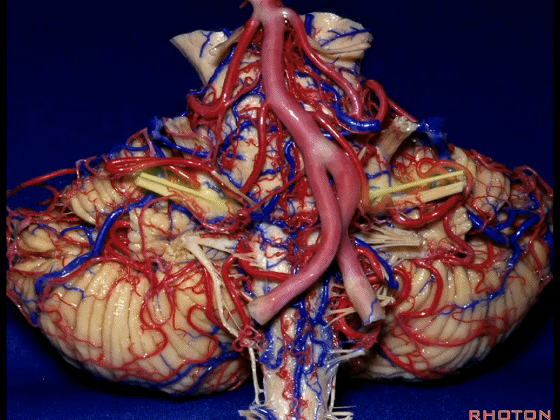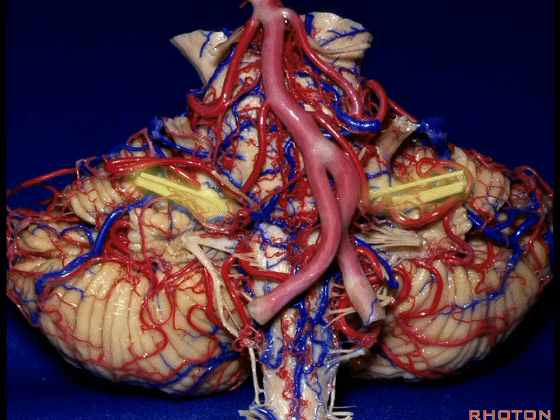
![]()
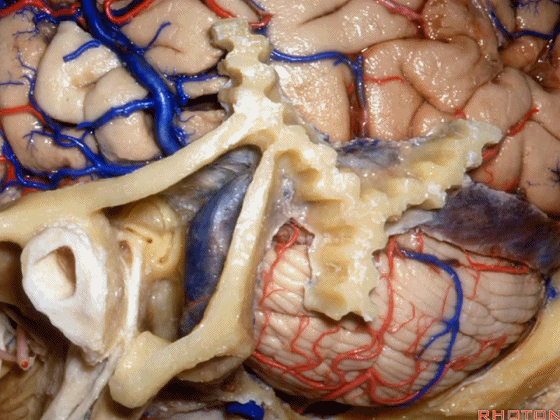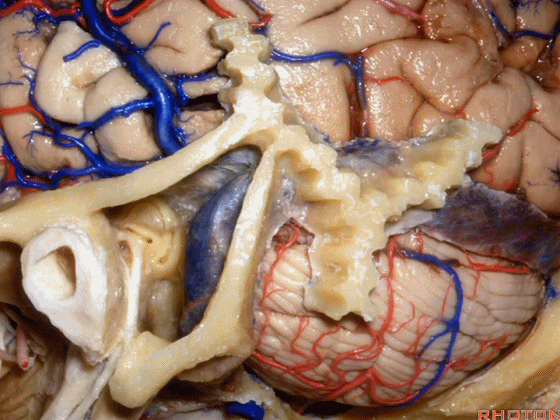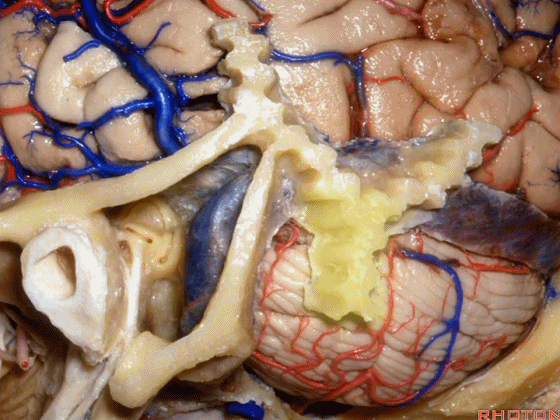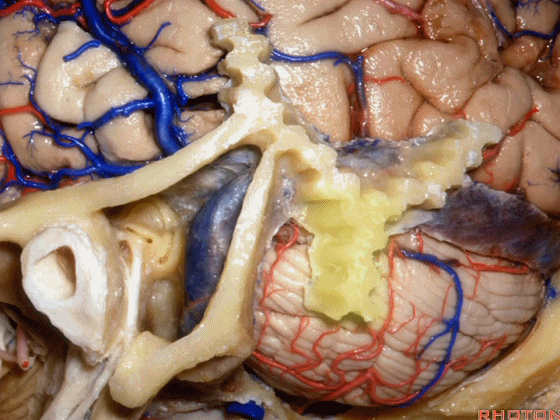
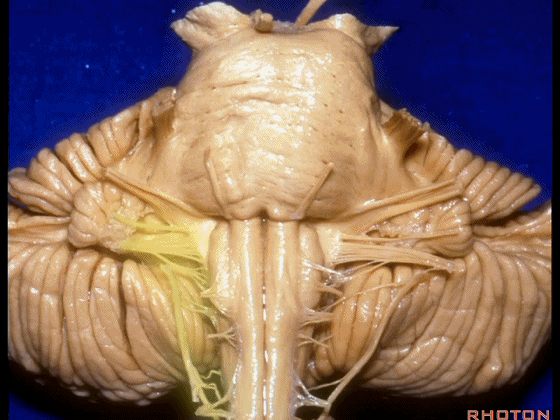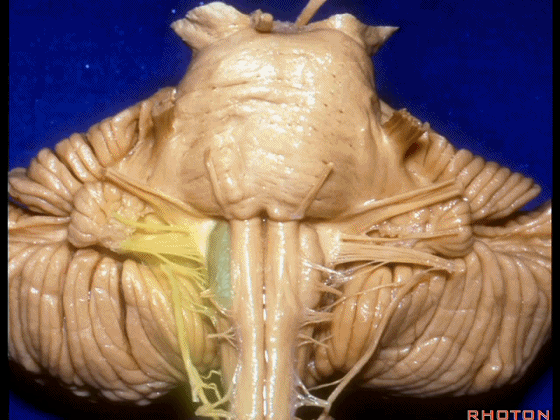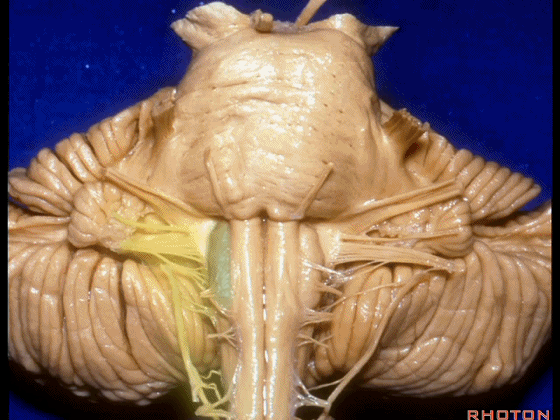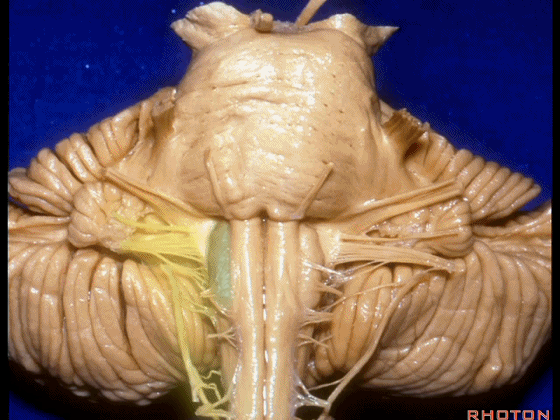
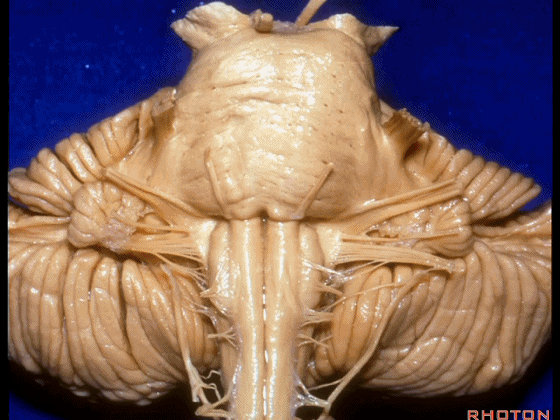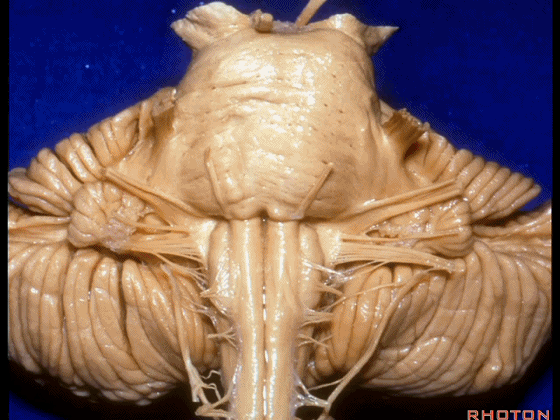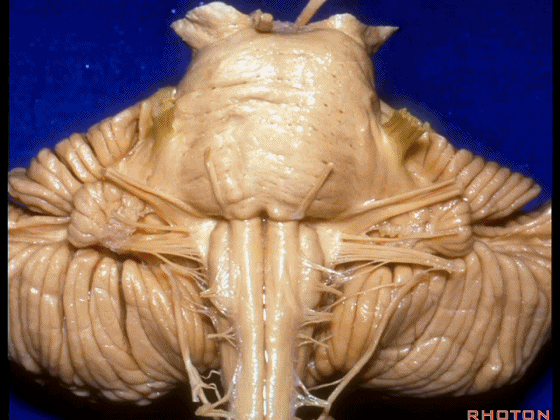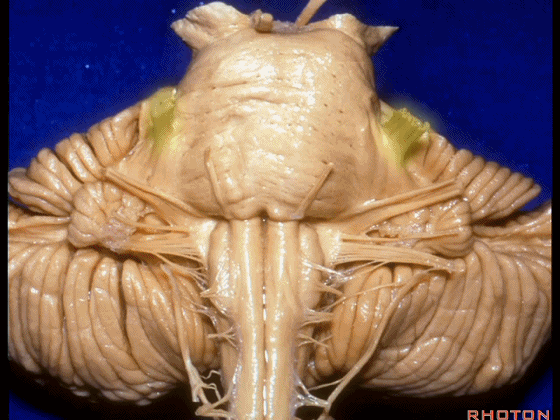
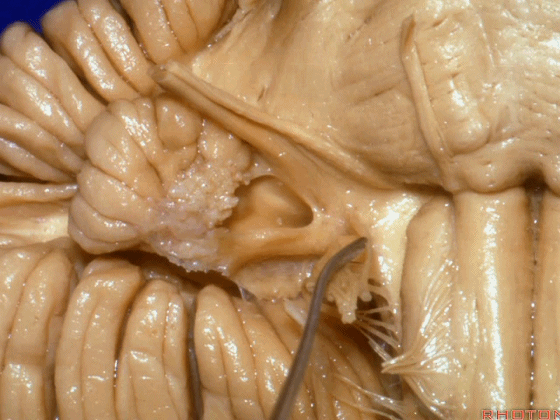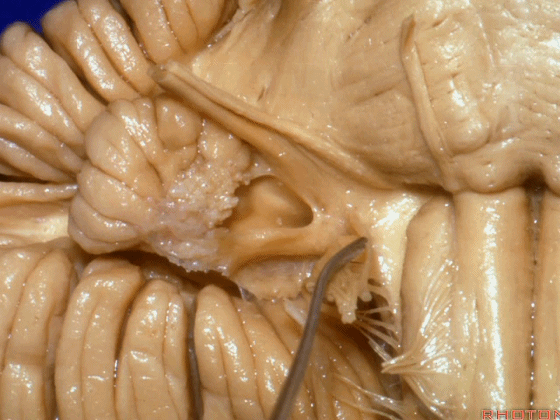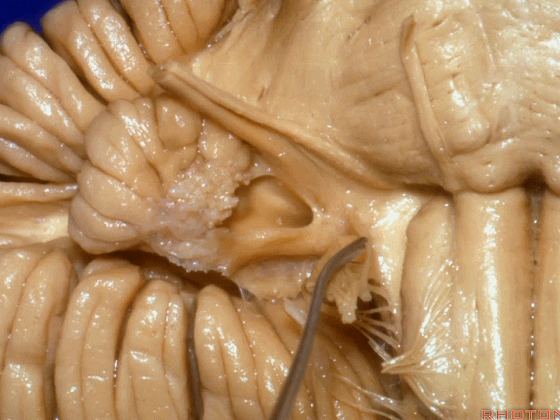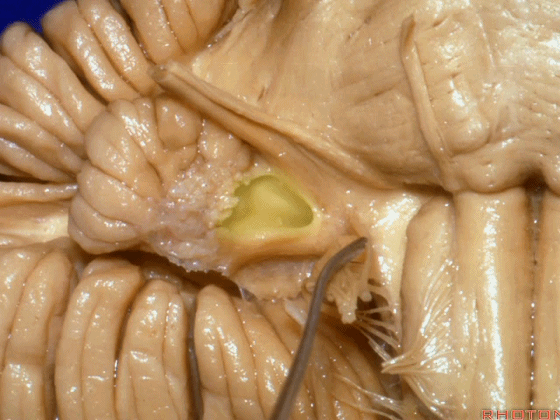
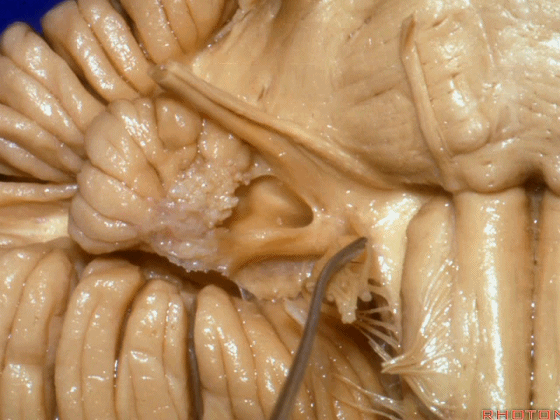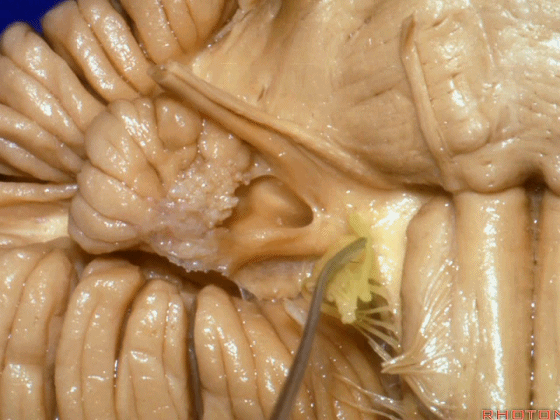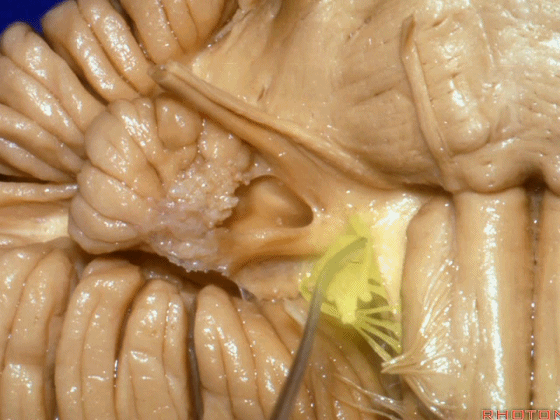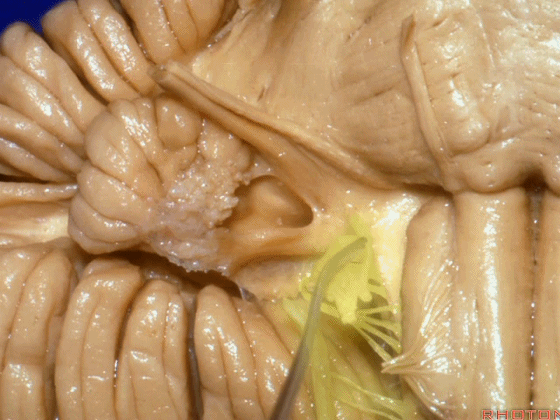
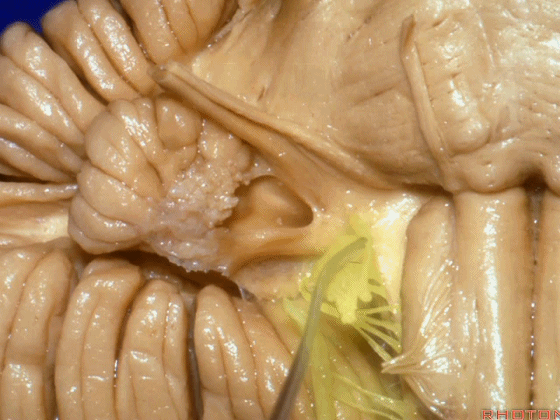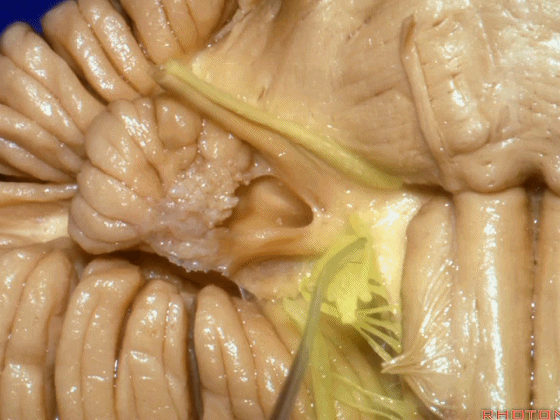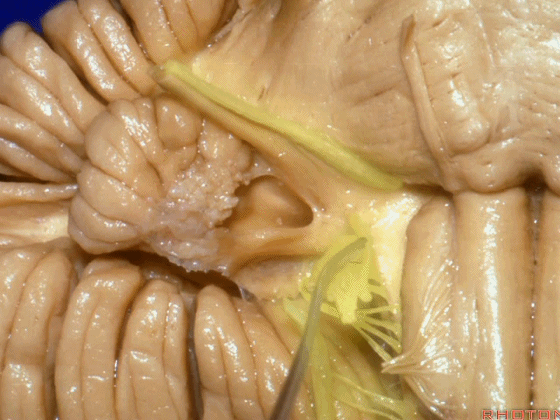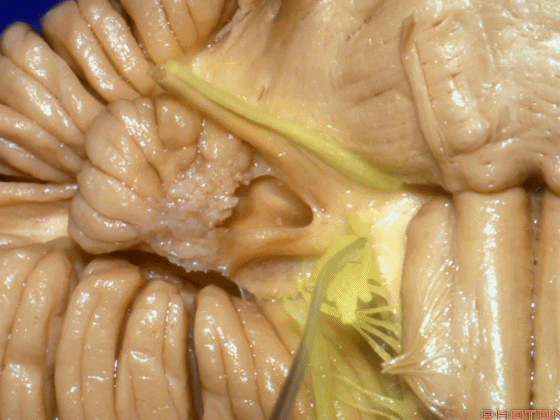
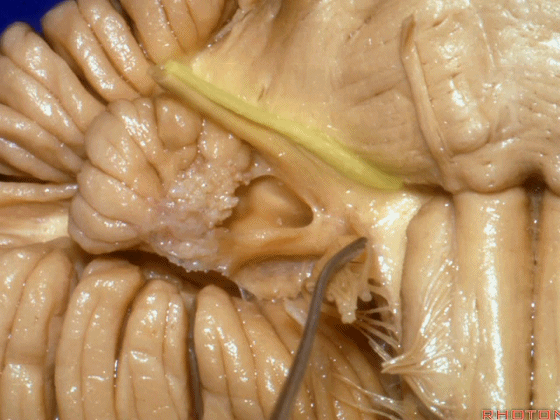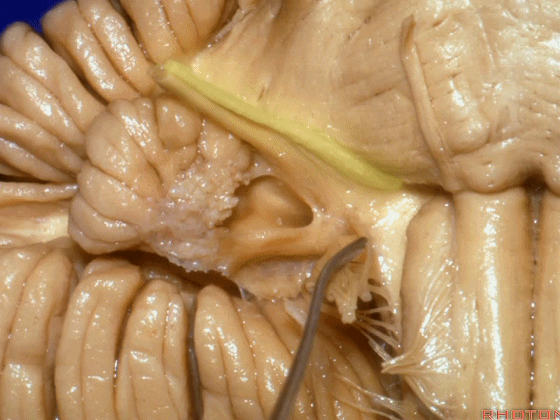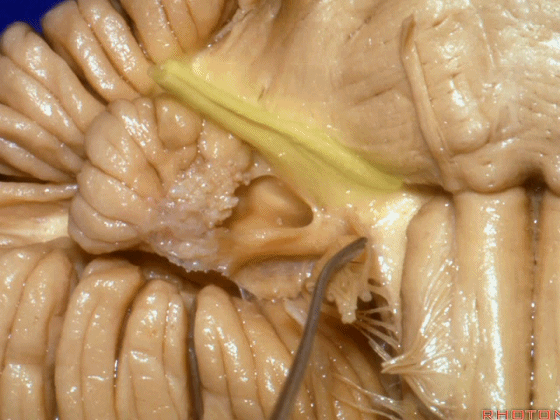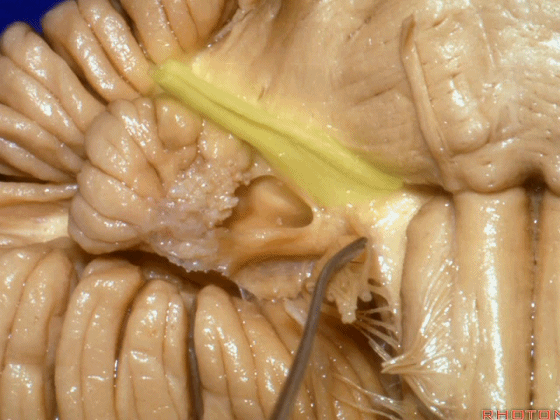
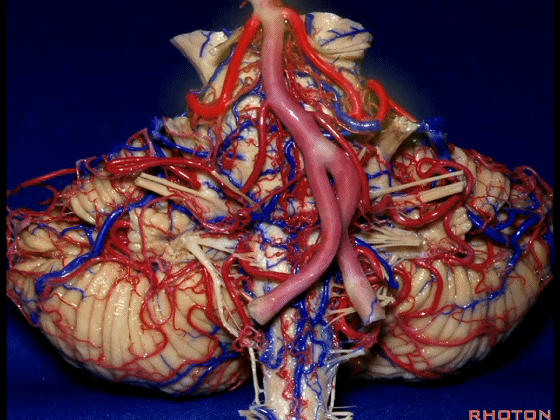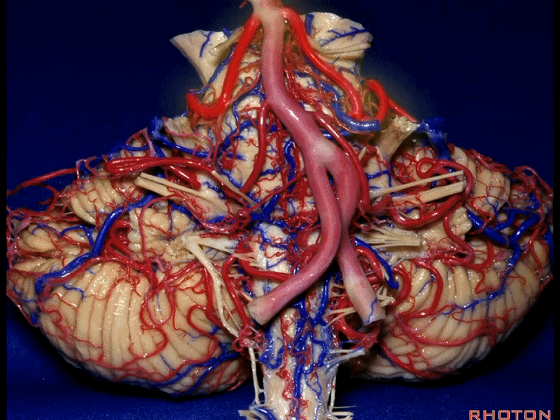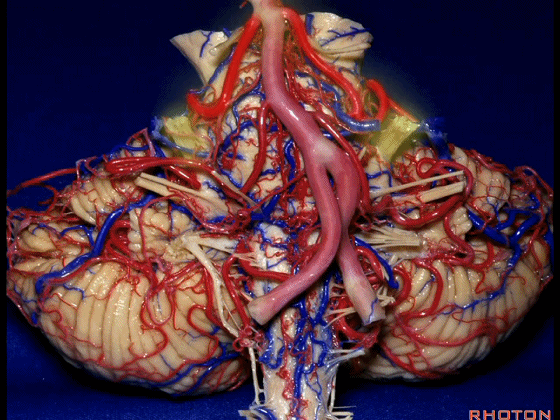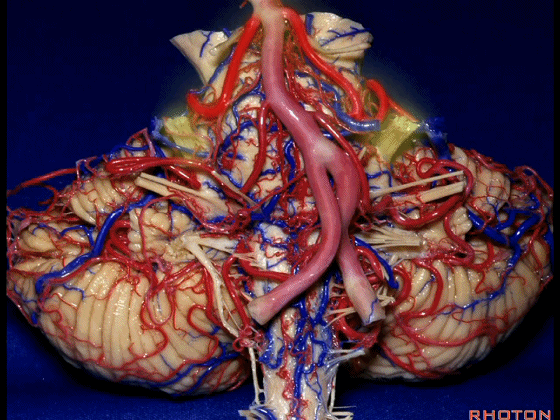
▼我们继续向下,来看看 桥小脑角(下图),它是小脑岩面包绕脑桥形成的。
Here we come down now we're looking at the CP angle. here where the petrosal surface folds around the lateral margin of the pons.
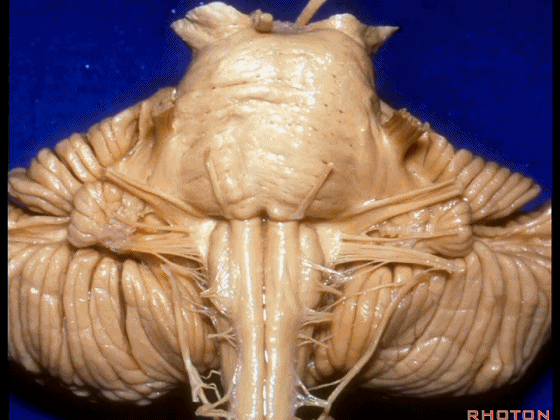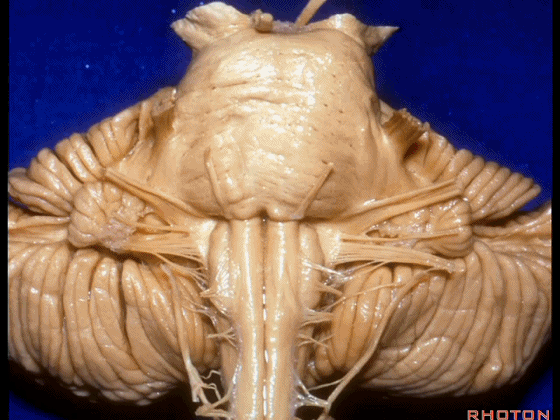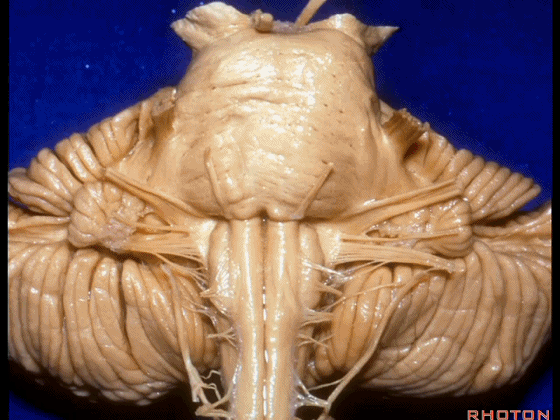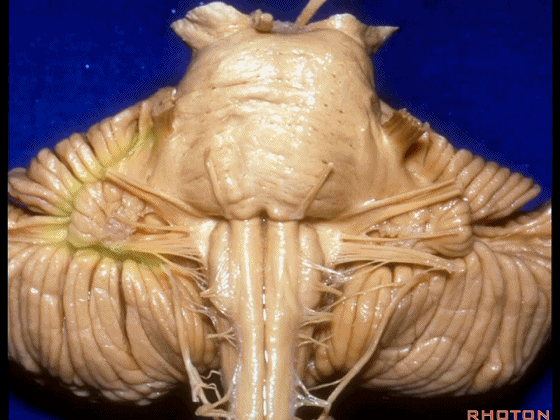
▼这是面神经(下图),从桥延沟的外侧端发出,走行于 脉络丛 及 绒球 的稍上方
And here we see VII arising at the lateral end of the sulcus between the pons and medulla and slightly above the choroidal plexus and flocculus,
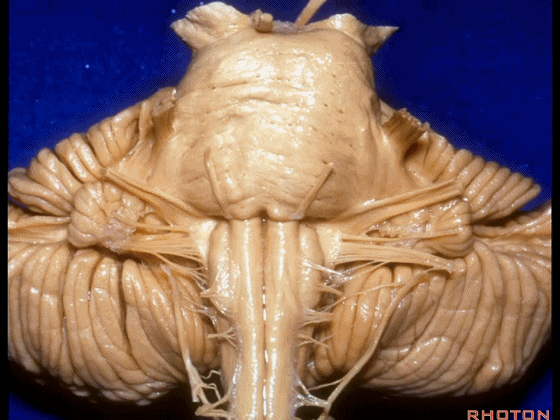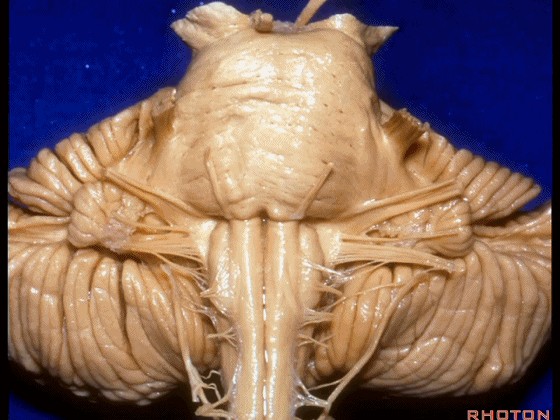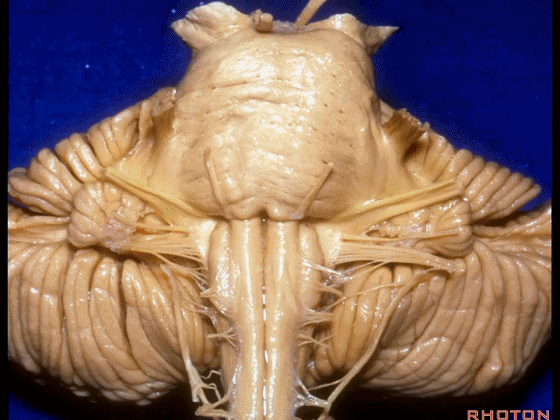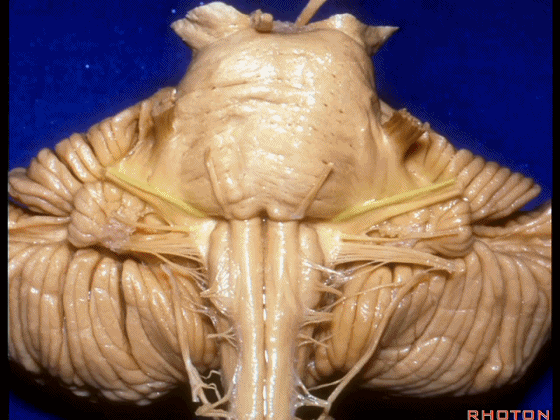
▼这是 脉络丛(choroidal plexus)
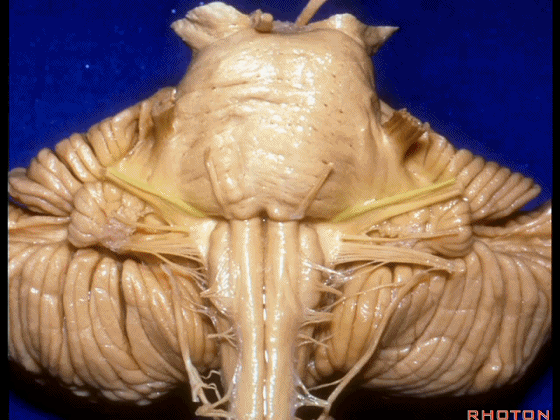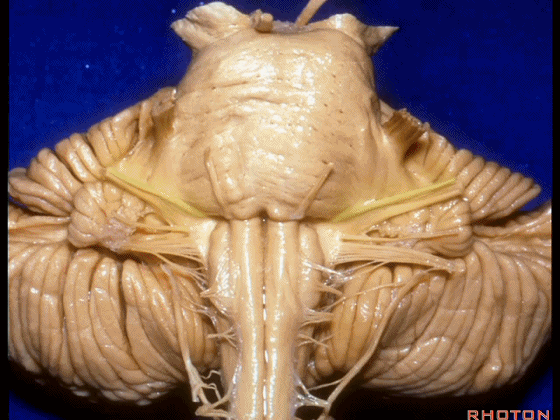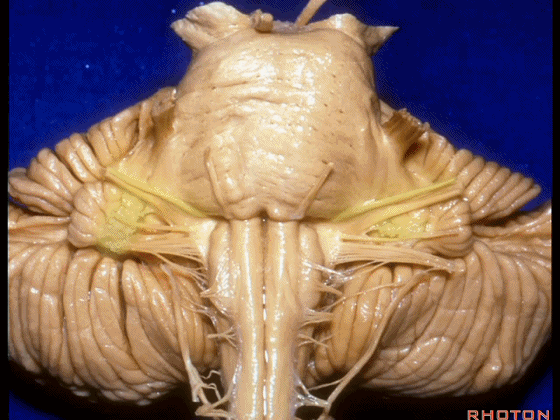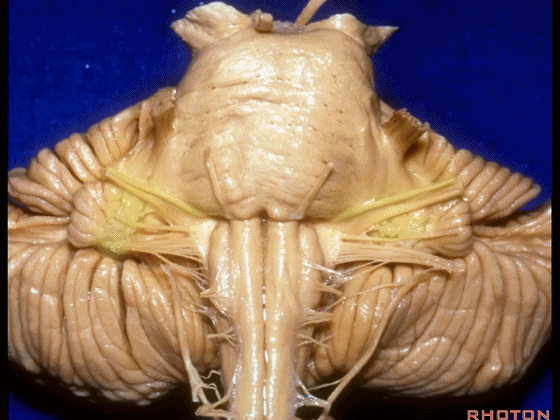
▼这是 小脑绒球(flocculus ['flɒkjələs])
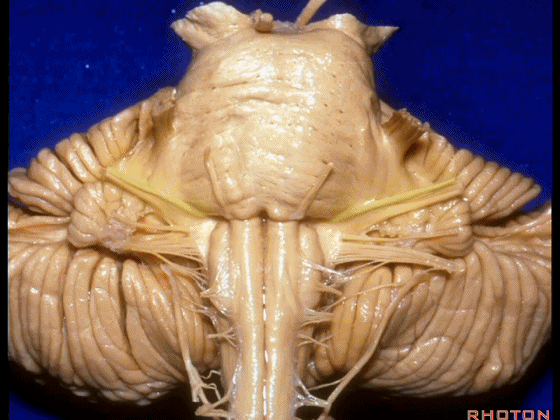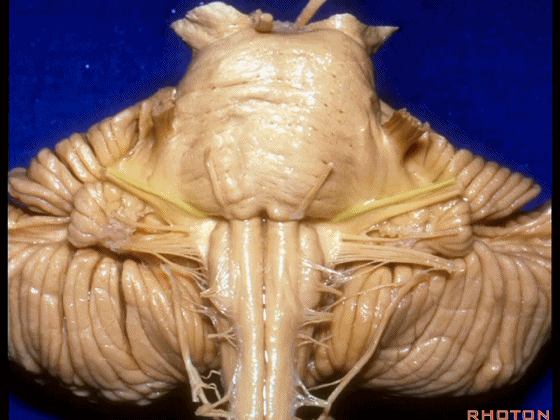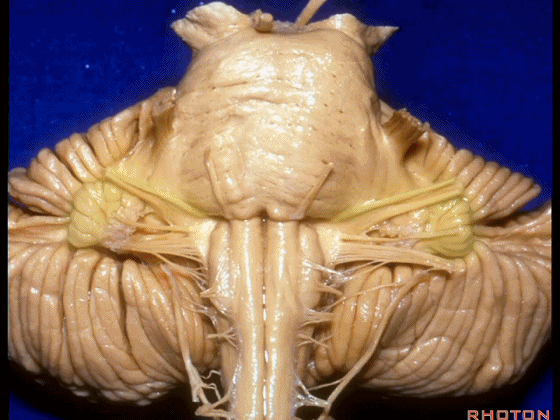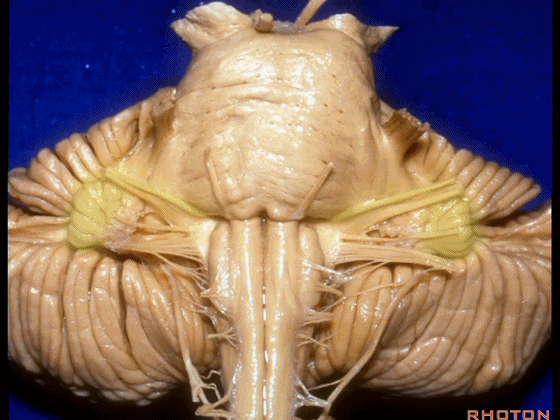
▼这是Luschka孔(第四脑室外侧孔,位于第四脑室两侧外侧隐窝尖端,与位于菱形窝下角尖部正上方的第四脑室正中孔一起引流第四脑室的脑脊液至蛛网膜下隙)。
hanging out Luschka.
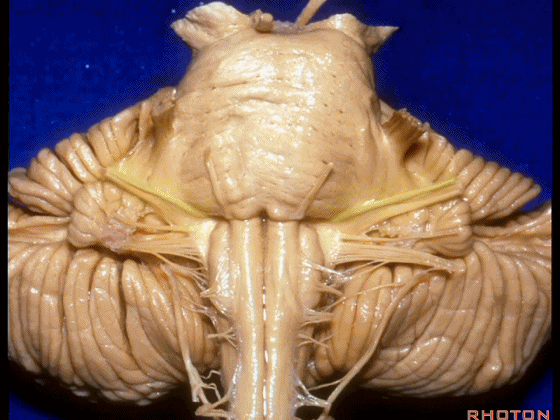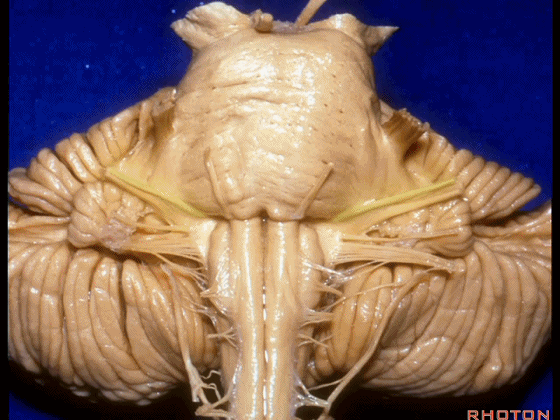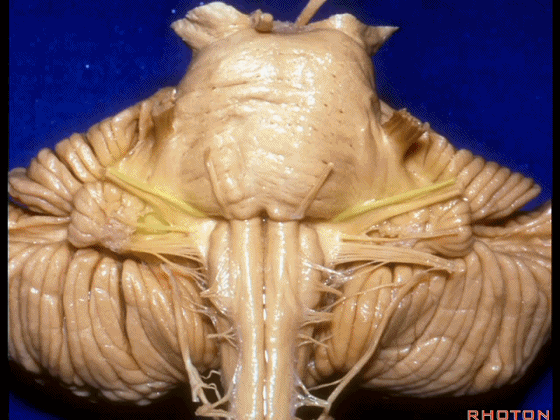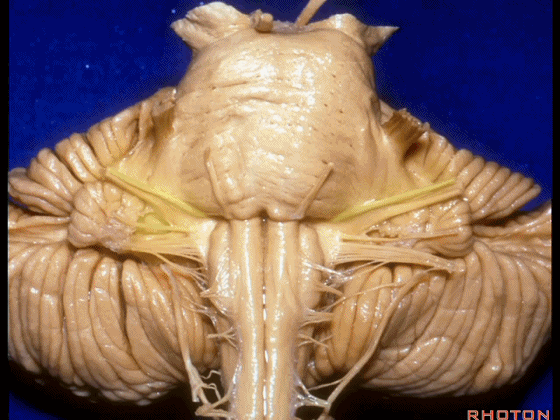
▼我们沿舌咽、迷走、副神经(下图)作一连线,并向上延长2~3毫米,即为面神经进入脑干处
And if you draw a line along, down along the arch of the IX, X, XI, and project that line up 2 or 3 millimeters, that's where VII enter the brainstem
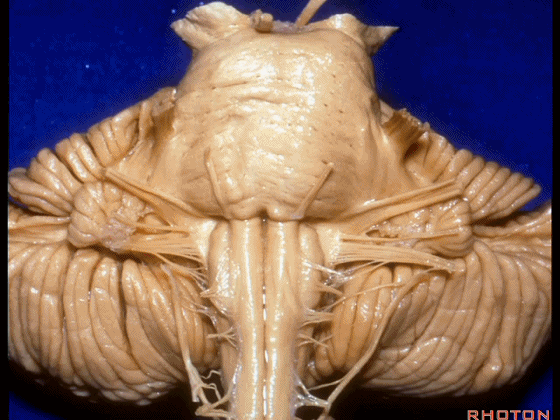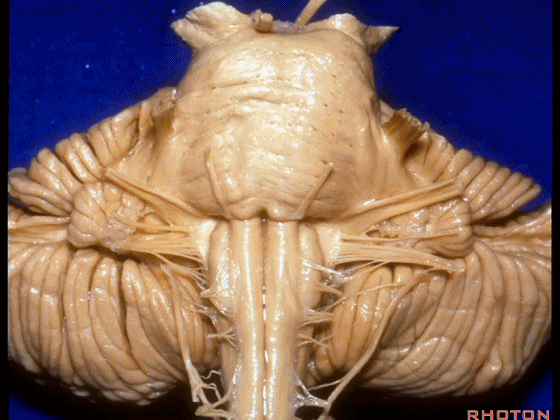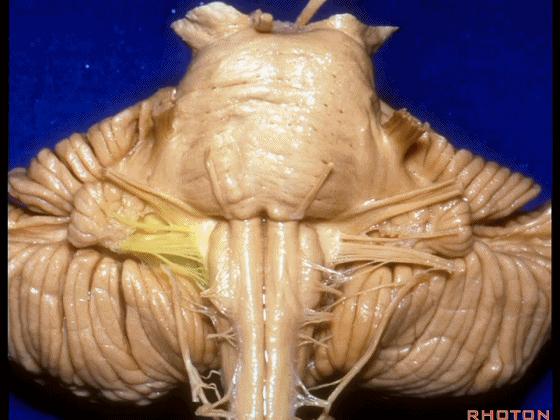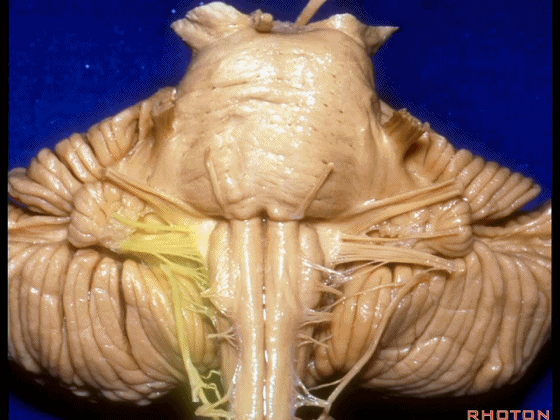
▼面神经进入脑干处,位于桥延沟的外侧端(下图)
at the lateral end of the sulcus between the pons and medulla.
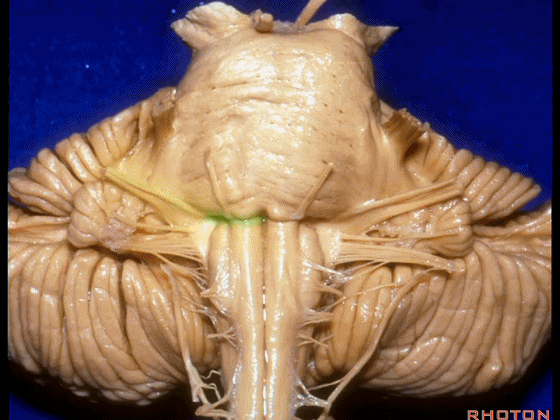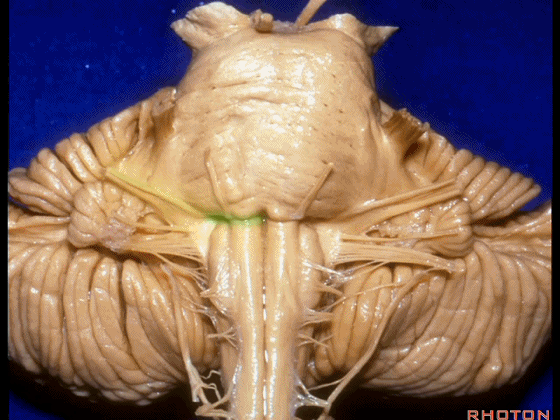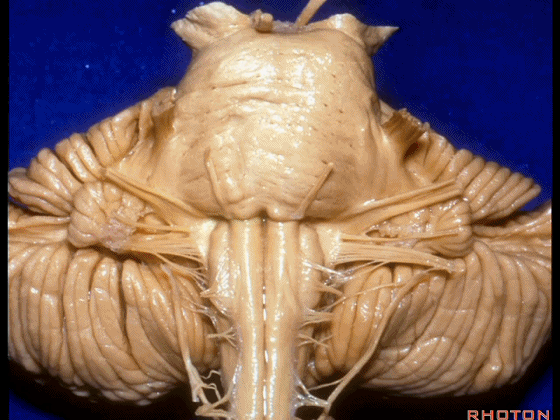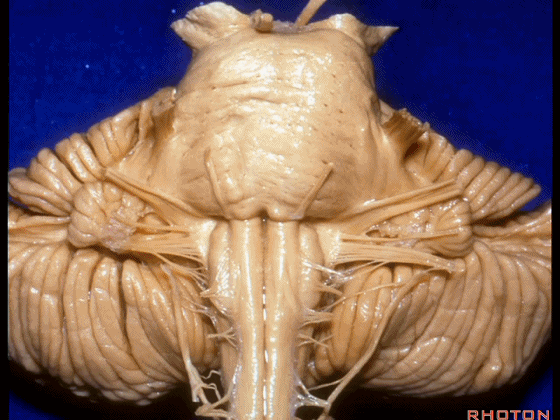
▼这里可见舌下神经位于橄榄核前方。
And here we see XII on the front of the olive,
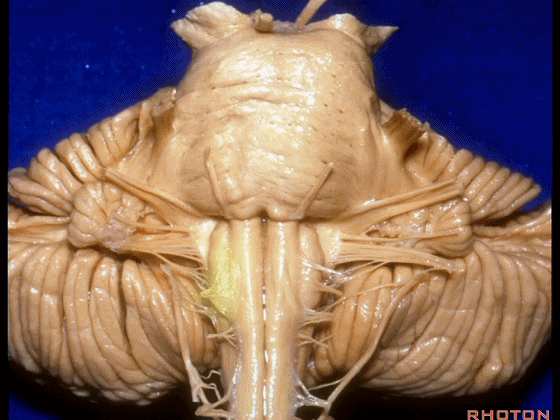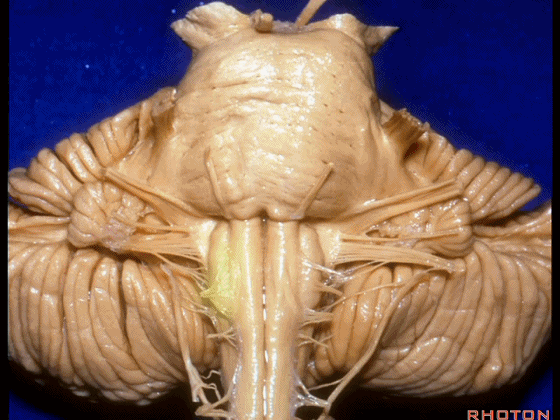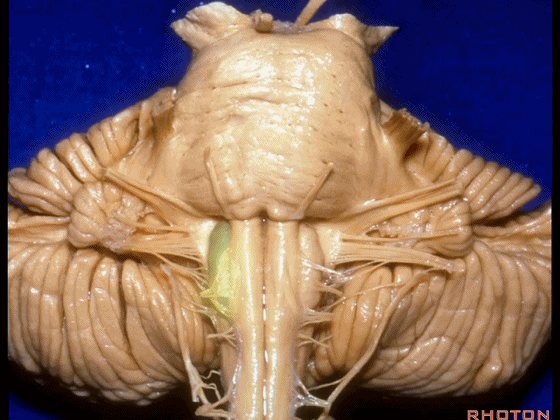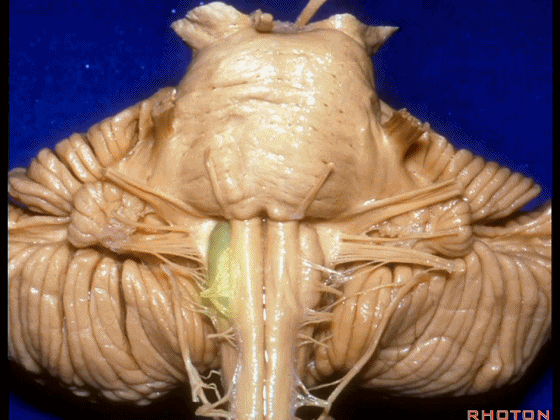
▼而舌咽、迷走、副神经从橄榄核后方发出。
and IX, X, XI arising on the back of the olive.
▼外展神经 从 桥延沟内侧段 发出。
We see VI arises in the medial part of the pontomedullary sulcus,

▼三叉神经 从 脑桥中部 水平发出。
and V arises at mid pontine level.
▼这是桥小脑角的局部观,下图示 Luschka孔
So, here's just CP angle. Luschka,
▼面神经、前庭蜗神经
VII、VIII
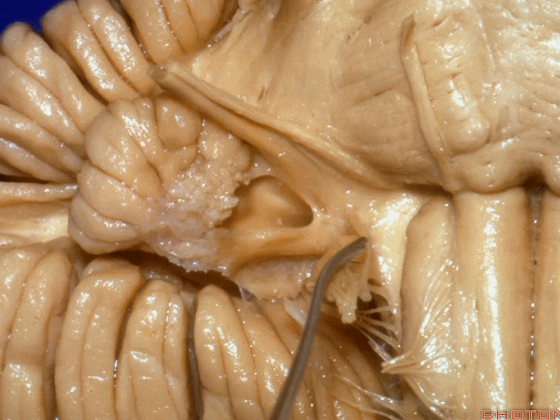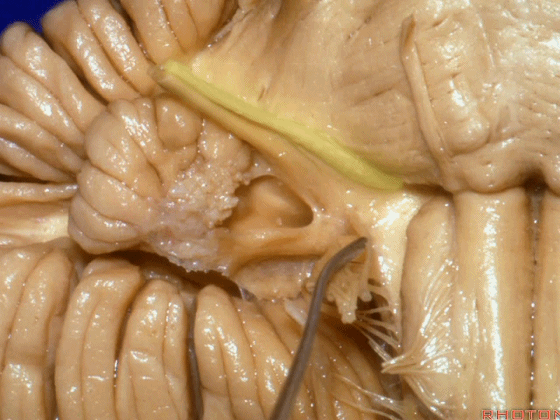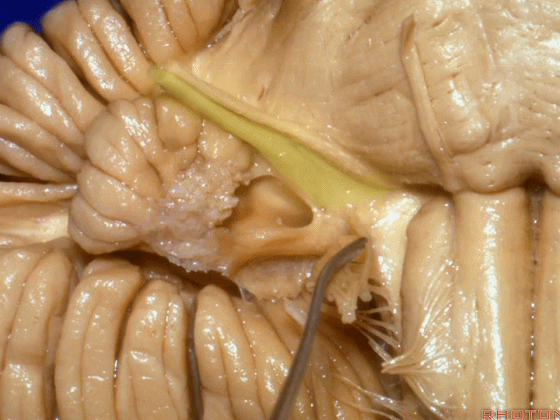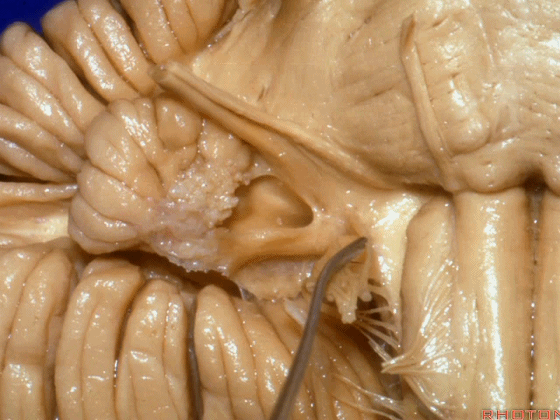
▼沿舌咽、迷走、副神经作一连线,向上延长2~3毫米,即为面神经进入脑干处,
You draw a line along the origin of these rootlets, go up 2 or 3 millimeters, and that's where VII enters the brainstem
▼面神经进入脑干处
▼面神经位于前庭蜗神经的前方。
in front of VIII.
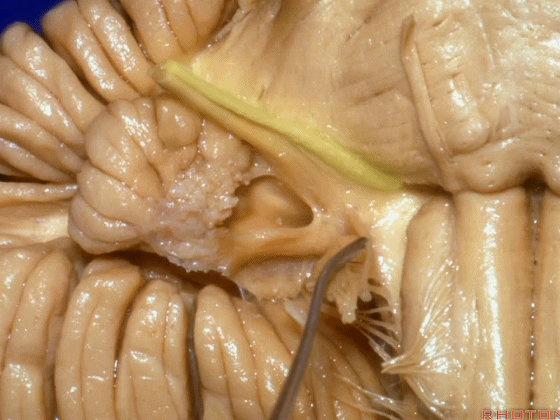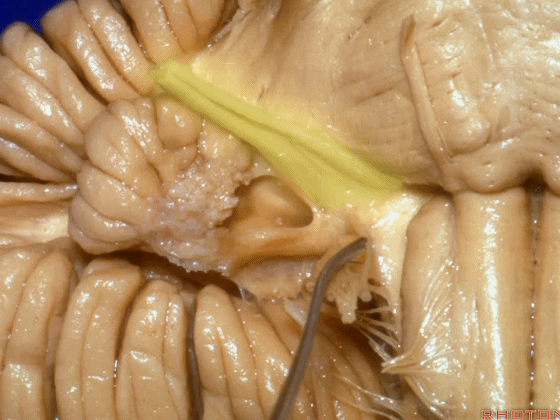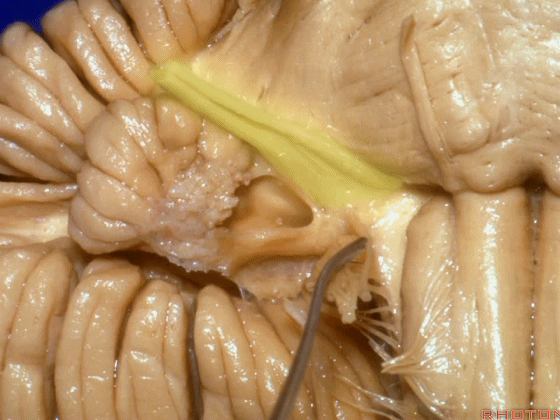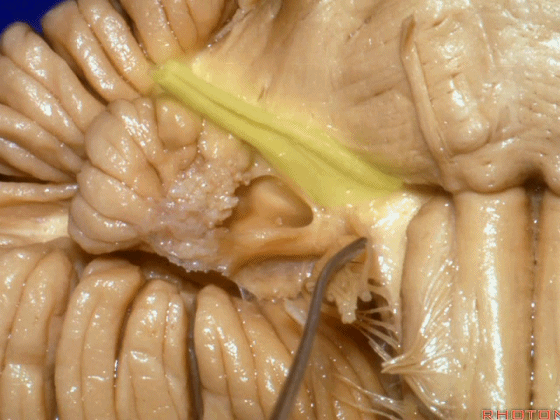
▼当从下图这个方向进行 绒球下入路时,在舌咽神经后方,向上即可见面神经。
And for the infrafloccular approach you come in this direction, behind IX, you look up and you see VII here.
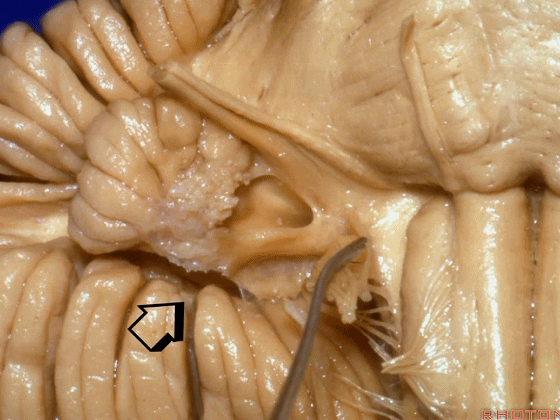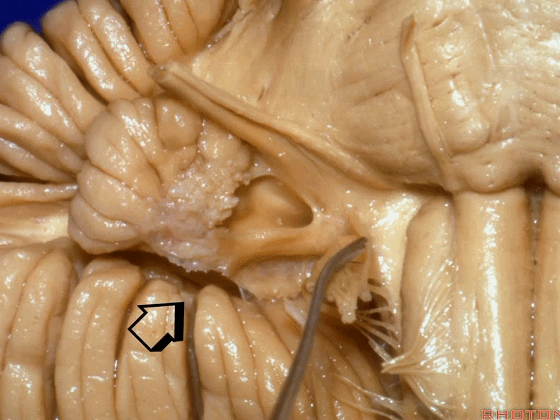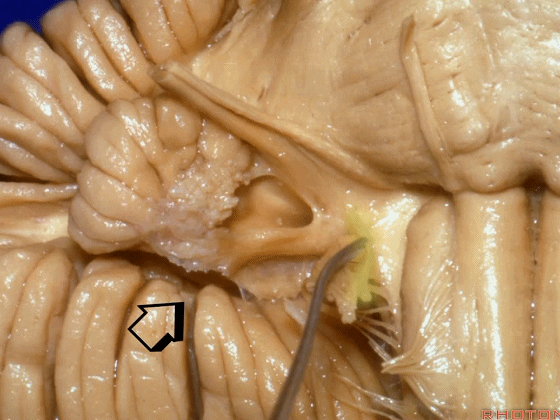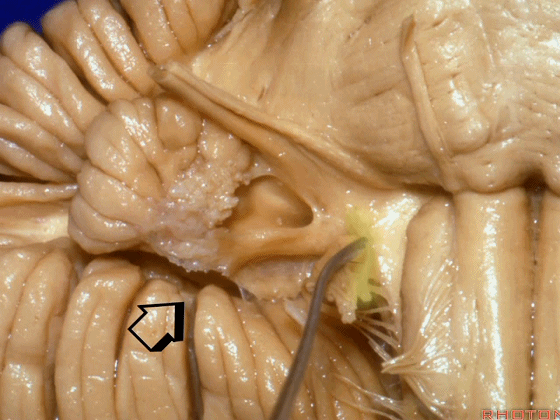
▼绒球下入路这一视角中,面神经似乎位于前庭蜗神经下方,实际上位于其前方。
As the view makes it look like it's below VIII, but it's really in front of VIII.
▼下面来看第二对 神经血管复合体:小脑前下动脉,起自脑桥水平
And just AICA arises at pontine level
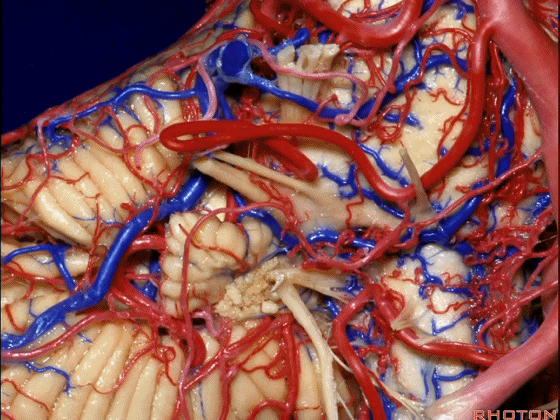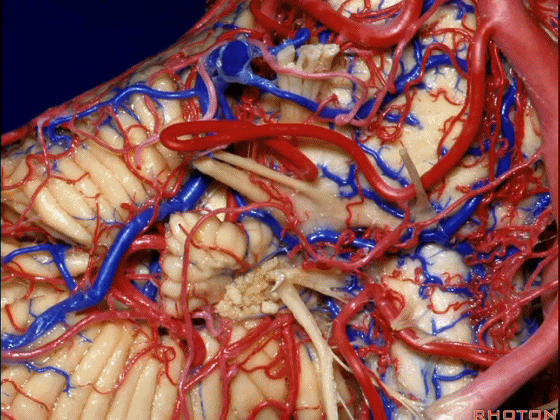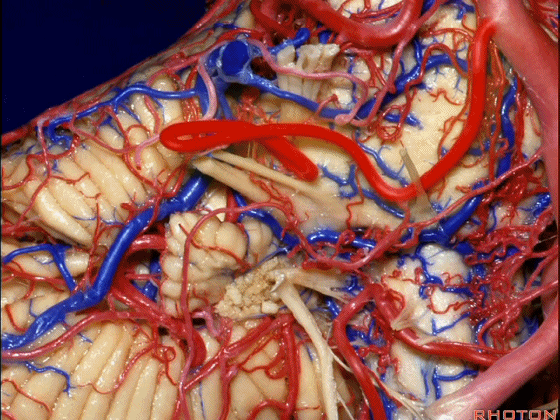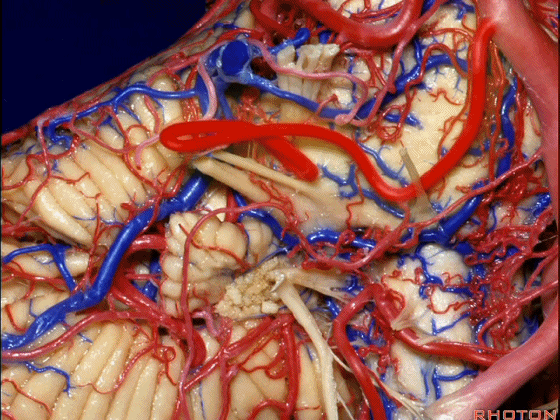
▼小脑前下动脉 越过 外展神经
passes by..what nerve? VI.
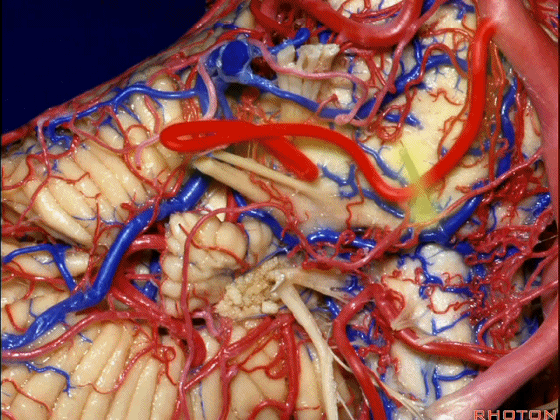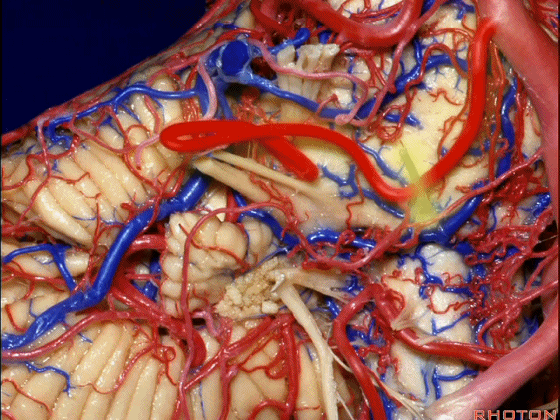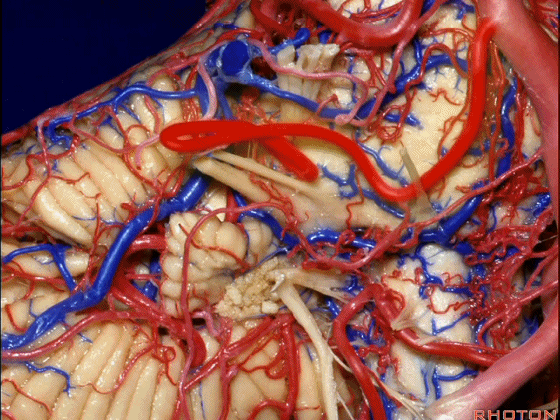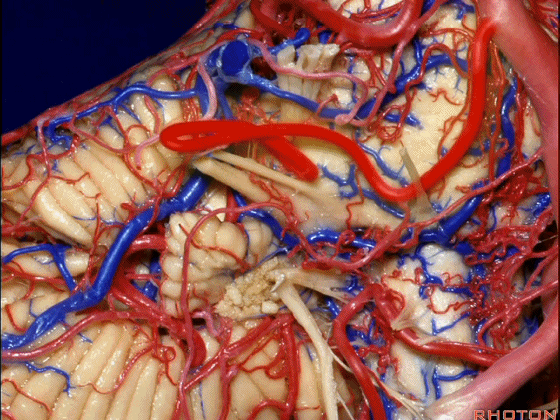
▼随后小脑前下动脉越过 面神经、以及前庭蜗神经。
Then VII, then VIII
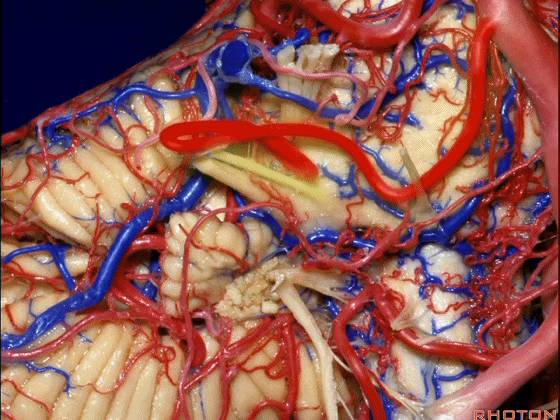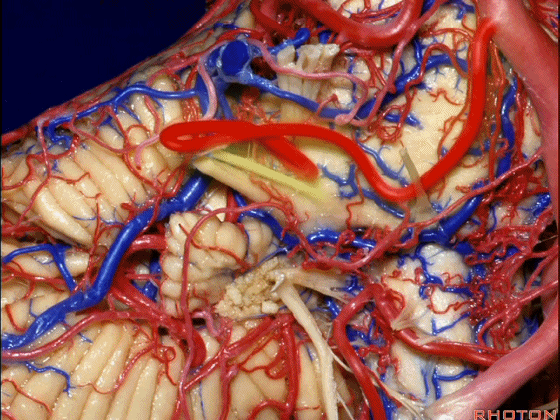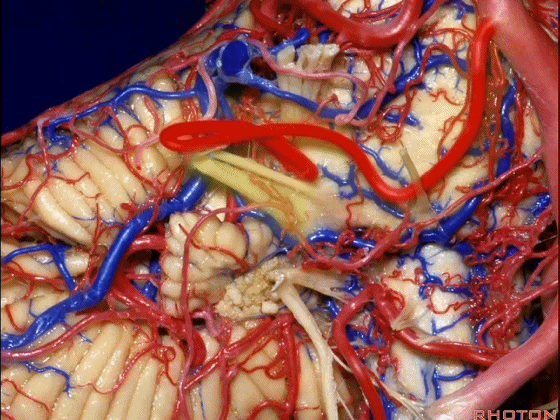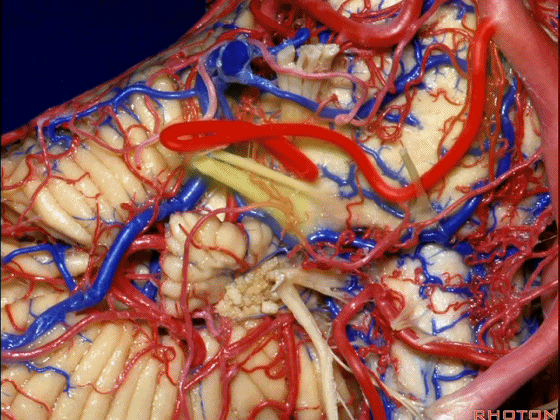
▼随后深入到的裂隙即所谓的 桥小脑裂 或 桥小脑角。小脑中脚构成桥小脑裂的底。随后,AICA供应小脑岩面的血供。
and then it dips into this cleft that we call the cerebellopontine fissure or angle. In the base of that cleft is the middle cerebellar peduncle. And then it supplies the surface that faces the back of the temporal bone.

▼在三叉神经痛微血管减压术中,通常情况下,年轻人群的小脑上动脉起自中脑水平,并绕行于下部中脑。
And here's what happens in trigeminal neuralgia,normally, early in life, this SCA arises at midbrain level,and it circles the lower midbrain.
▼而随着年龄增长,这条动脉向下迂曲,术中可见其从上方压迫三叉神经,或更为向下迂曲而从腋下压迫三叉神经。
But with age, this artery loops downward and in trigeminal neuralgia we find it, often find it sitting here on top of the trigeminal nerve, or loop down into the axilla of the trigeminal nerve.
▼这是面神经和前庭蜗神经。
Here's VII and VIII.
▼这是小脑前下动脉。
The AICA is here.
▼再让我们看看面肌痉挛术中所见。小脑前下动脉(下图)可向下迂曲压迫面神经。
And here's what can happen in hemifacial spasm.You can have an AICA loop down here next to VII at the junction with the brainstem.
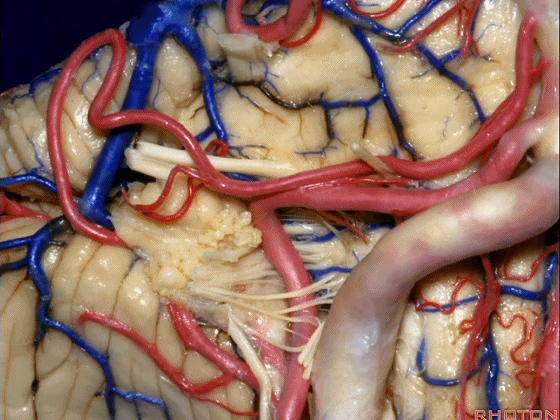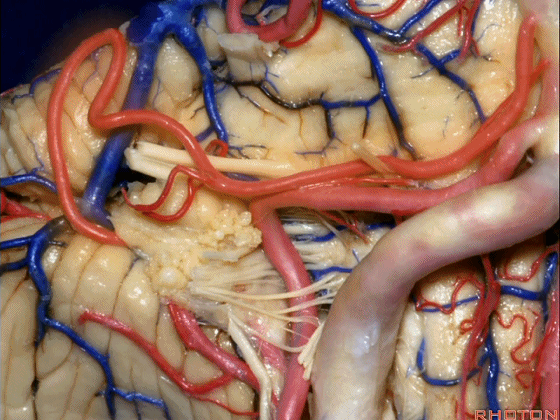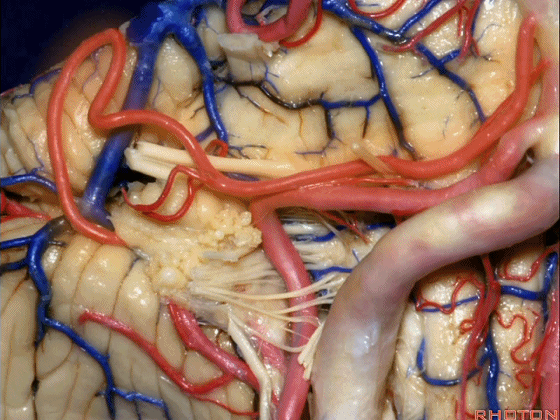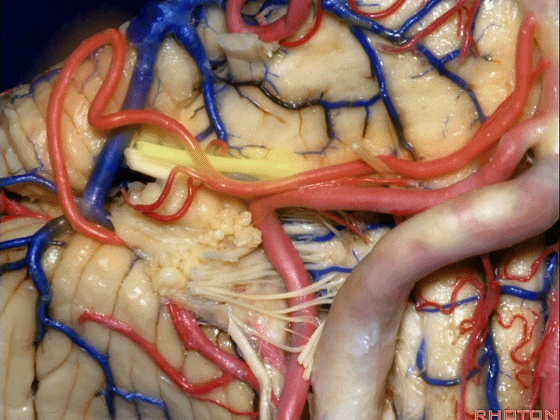
▼约另一半病例,则可见小脑后下动脉(下图)向上迂曲压迫面听神经
Or in about half the cases, the PICA will loop upward under VII and VIII,
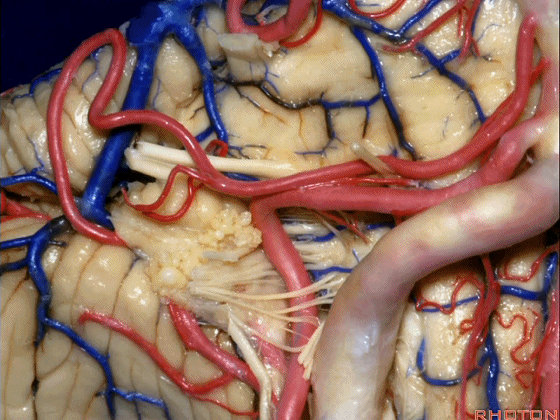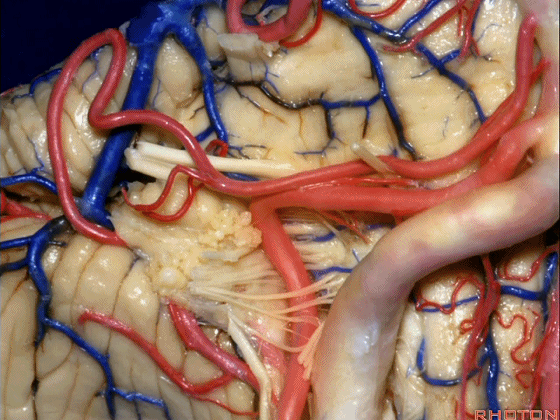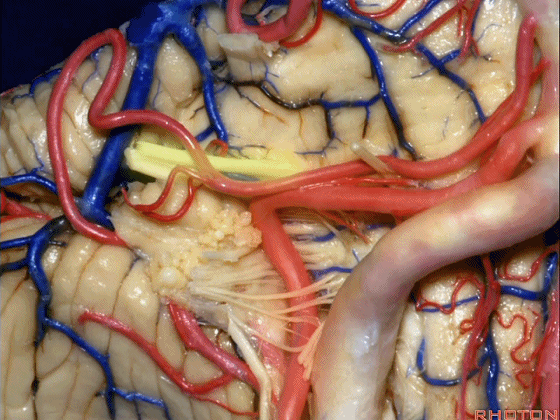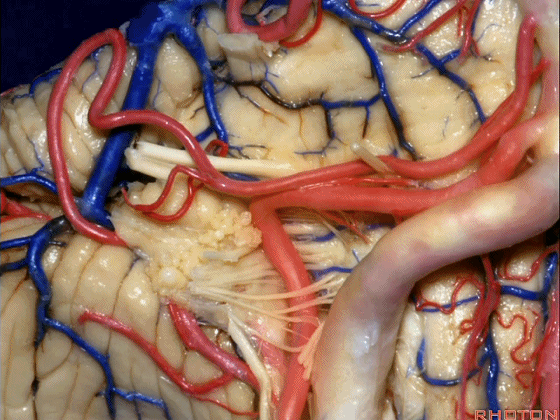
▼小脑后下动脉(下图)随后下行并从背侧穿行于舌咽神经与迷走神经之间。
and then it'll pass downward and it then passes dorsally some place between IX and the rootlets of XI.
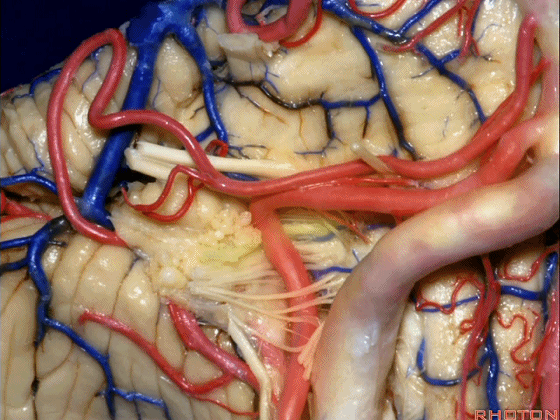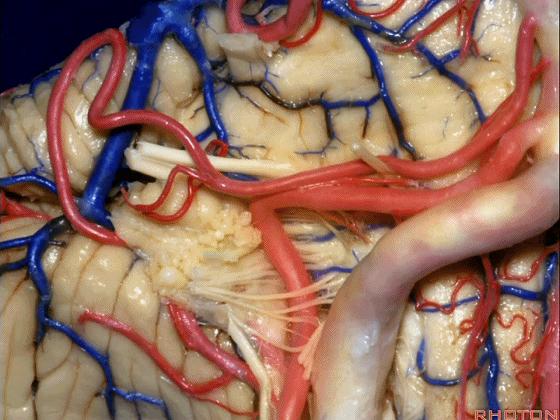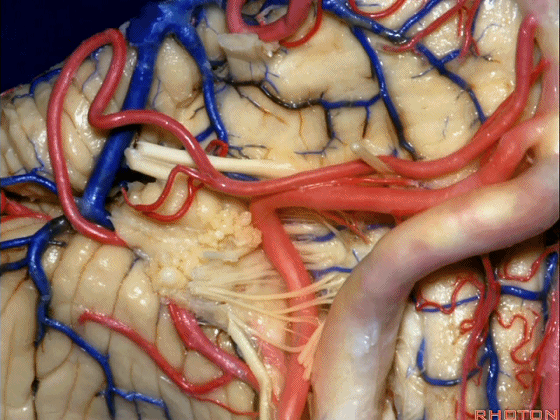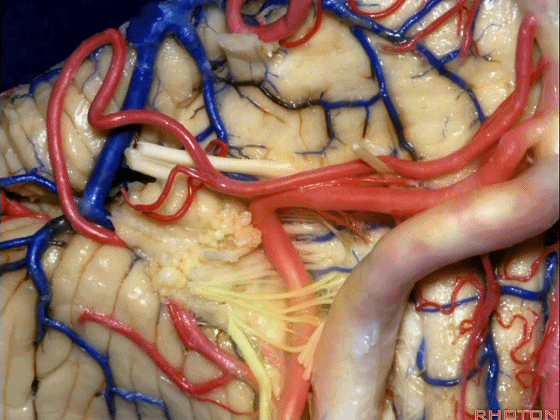
▼小脑后下动脉可从背侧走行,此处(下图)看起来似乎在迷走神经和副神经下方,然后行向背侧。实际上它可穿行于舌咽神经至副神经之间的任何部位。
It can be passing dorsal.Here it looks like it's below between X and XI that it passes then dorsally to the nerves. But it can be any place between IX and XI.


颞骨解剖(后颅窝部分)
Navigating the Temporal Bone, Posterior fossa
▼接下来看看内听道口(porus 下图)的解剖。
Just looking at porus.

▼这是面神经
We see VII,

▼这是前庭蜗神经
VIII.

▼这是弓状下动脉(72%的脑中存在。在内听道口的内侧从AICA发出,穿过弓状下窝表面的硬脑膜进入弓状下管,供应半规管处的岩骨)
We see subarcuate artery,

▼这是迷路动脉(进入内听道后分支供应内听道骨壁和覆盖其表面的硬脑膜、内听道内的神经、前庭、耳蜗和内耳等结构)
labyrinthine artery,

▼面神经(下图)位于小脑绒球下
facial nerve in the infrafloccular position,

▼Luschka孔

点击继续阅读
颞骨解剖(后颅窝部分)与桥小脑角区---Rhoton解剖视频学习笔记系列(下)




